Figure 2: Design strategies and functionalization of NANPs.
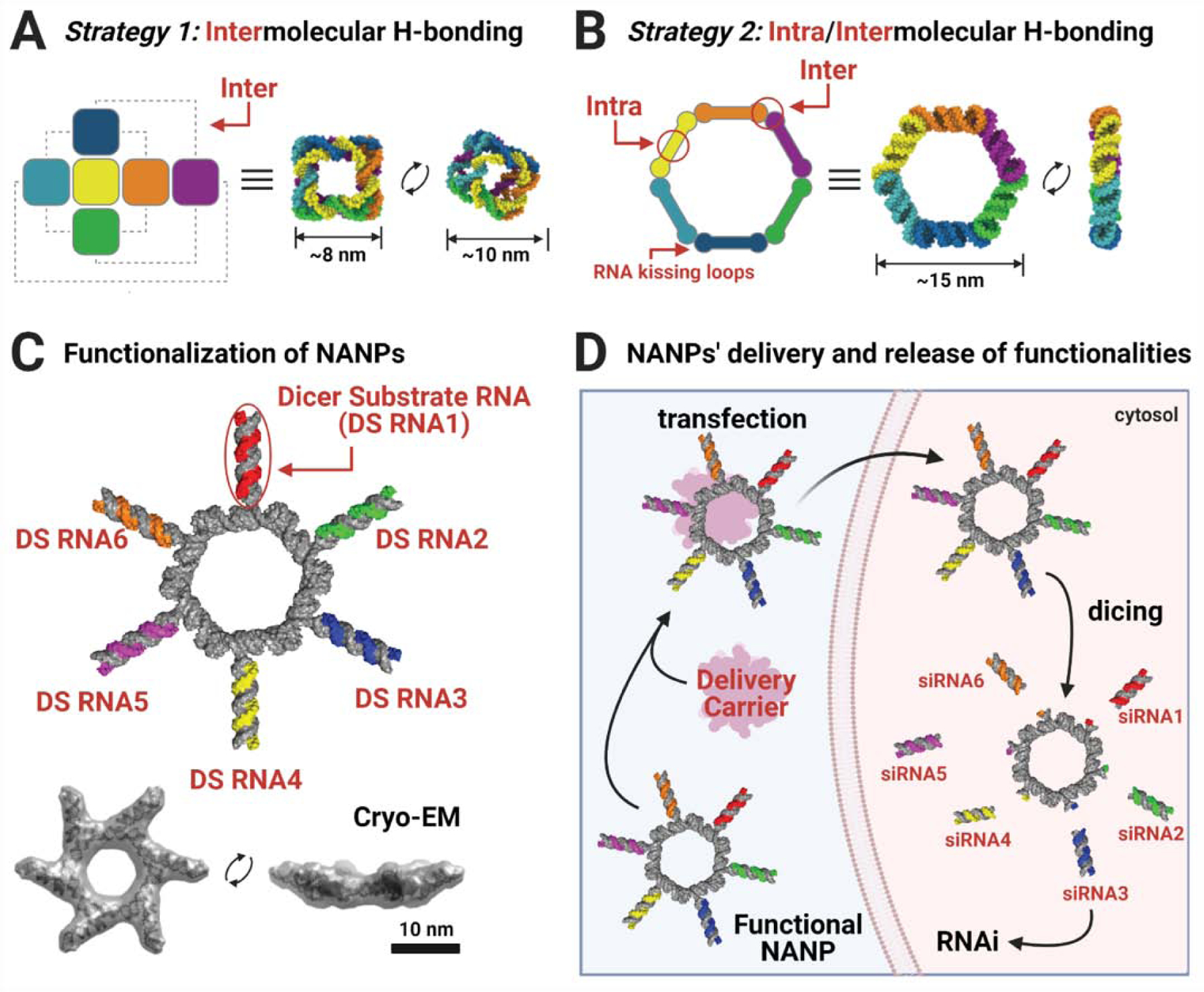
(A) For the formation of cubes, intermolecular hydrogen bonds occur between six oligonucleotides. As these are canonical WC bps, the cubes may be composed of any combination of RNA and/or DNA. (B) For the formation of rings, intramolecular hydrogen bonding first occurs within each strand, exposing single-stranded regions (RNA kissing loop motifs) which can then interact intermolecularly. (C) By extending the sequences in their compositions, NANPs can be functionalized with Dicer Substrate (DS) RNAs which can then enter the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. Due to their hexameric nature, up to six DS RNAs can be added to each ring for simultaneous knockdown of six different target genes. Cryo-EM (from ref. [119]) demonstrates the structure of the functional RNA rings. (D) Functional NANPs must be combined with a delivery carrier for their transfection into cells, where they may then be processed by Dicer to begin RNAi. Created with Biorender.com.
