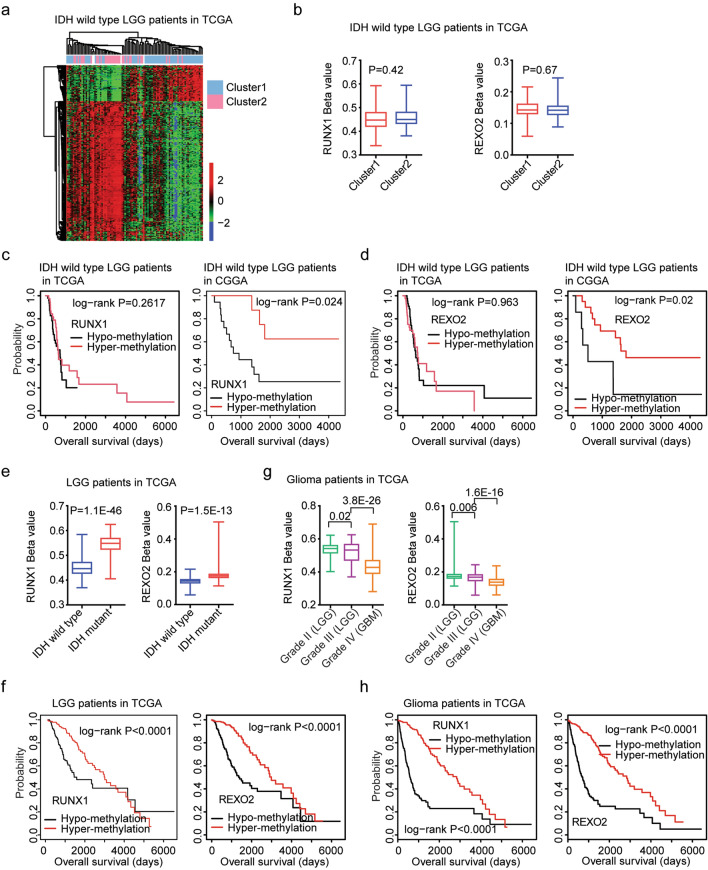
Figure 7.
RUNX1 and REXO2 hyper-methylation are associated with the favorable clinical outcomes of IDH wild type LGG or LGG or glioma patients. (a) Un-supervised clustering heatmaps demonstrated the differentially methylated genes between sub-cluster1 and sub-cluster2 IDH wild type LGG patients in TCGA dataset. Red represented the hyper-methylated genes and blue represented the hypo-methylated genes. (b) Box plots showed the methylation levels of RUNX1 and REXO2 in sub-cluster1 and sub-cluster2 IDH wild type LGG patients in TCGA dataset. (c) The Kaplan–Meier Plotters demonstrated the different clinical outcomes of IDH wild type LGG patients with RUNX1 hypo-methylation or with RUNX1 hyper-methylation in TCGA and CGGA datasets. (d) The Kaplan–Meier Plotters demonstrated the different clinical outcomes of IDH wild type LGG patients with REXO2 hypo-methylation or with REXO2 hyper-methylation in TCGA and CGGA datasets. (e) Box plots showed the methylation levels of RUNX1 and REXO2 in LGG patients with (red) or without (blue) IDH mutations in TCGA dataset. (f) The Kaplan–Meier Plotters showed the correlations of RUNX1, REXO2 methylation levels and LGG overall survival in TCGA dataset. (g) Box plots demonstrated the methylation levels of RUNX1 and REXO2 in grade II (LGG), grade III (LGG) or grade IV (GBM) glioma patients in TCGA dataset. (h) The Kaplan–Meier Plotters showed the correlations of RUNX1, REXO2 methylation levels and glioma overall survival in TCGA dataset.