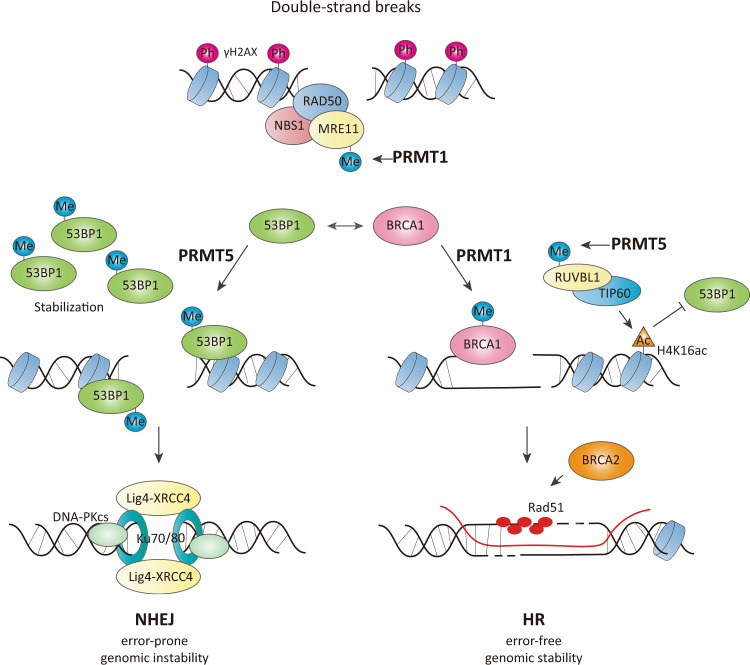
Fig. 4. Regulation of the DNA damage response through protein arginine methylation.
Under DNA double-strand breaks, the MRE11–RAD50–NBS1 complex is recruited into the DNA lesion and activates ATM/CHK2 kinase signaling. PRMT1-mediated MRE11 methylation is essential for exonuclease activity and localization to DNA. There are two main repair pathways, homologous recombination (HR) and nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ). 53BP1, a major regulator of NHEJ, is competitively methylated by PRMT1 and PRMT5 in the GAR motif. PRMT1-mediated methylation of 53BP1 promotes DNA binding (not shown), and PRMT5-mediated methylation increases the stability of 53BP1, which contributes to NHEJ repair. BRCA1, a well-established key regulator of HR, is methylated by PRMT1, but its role is unknown. Arginine methylation of RUVBL1 (a cofactor of the TIP60 complex) by PRMT5 facilitates TIP60α-dependent histone H4 Lys16 acetylation (H4K16ac), which blocks 53BP1 recruitment to reinforce HR.