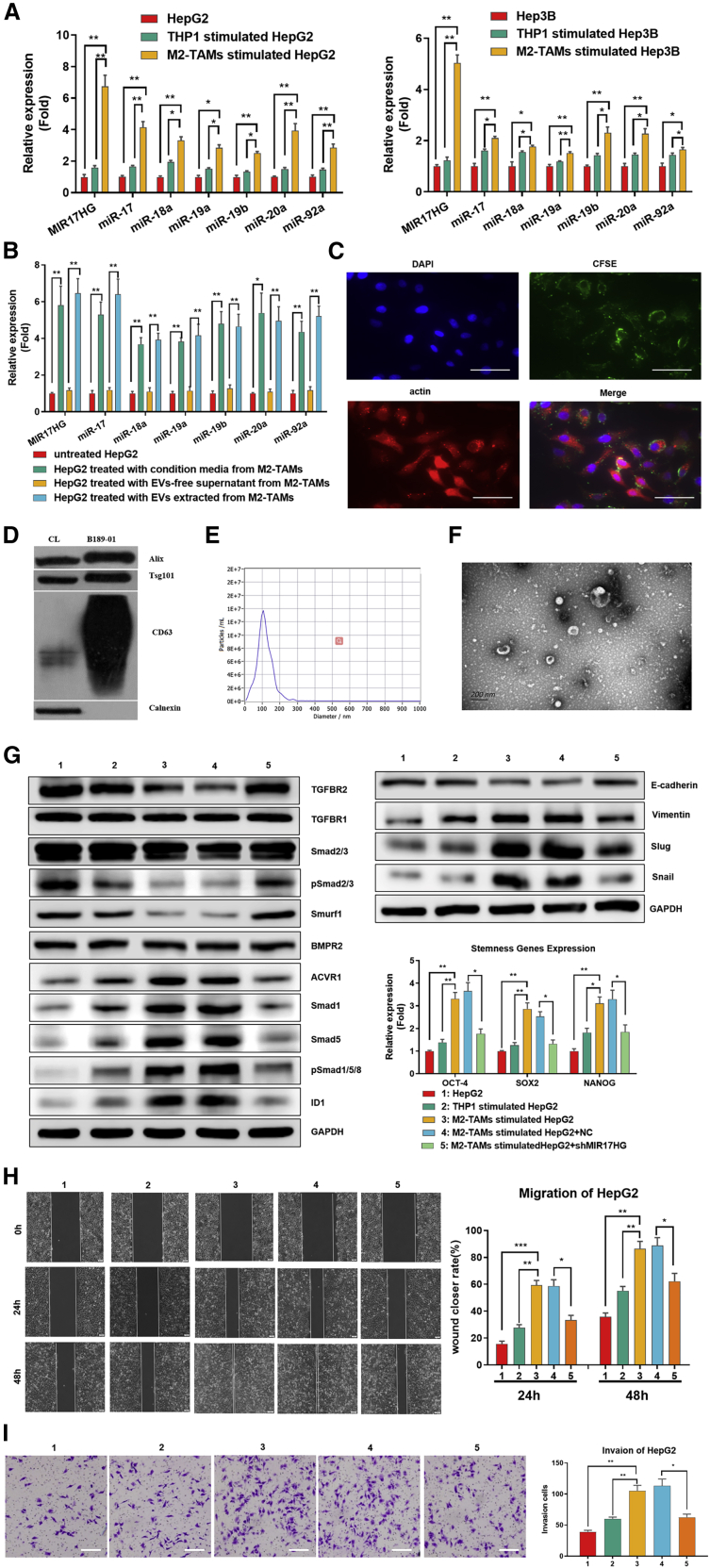
Figure 7.
M2-TAMs increased the levels of the MIR17HG and miR-17-92 cluster in HCC cells via EVs to exacerbate the imbalance of the TGF-β1/BMP-7 pathways
(A) PCR array for the expression of the MIR17HG and miR-17-92 cluster in HepG2 and Hep3B cells cocultured with M2-TAMs compared to THP-1 cells cocultured or cultured alone. (B) The expression of the MIR17HG and miR-17-92 cluster in HepG2 cells was detected by PCR after treatment with EVs from M2-TAMs or EV-free supernatant from M2-TAMs or conditioned media from M2-TAMs. (C) HepG2 cells were treated with CSFE-labeled EVs secreted by M2-TAMs, and HepG2 cells were visualized by staining with DAPI and actin. Scale bars, 50 μm. (D) Western blotting of specific membrane proteins from control cells and EV lysates from M2-TAMs. (E) NTA of EVs from M2-TAMs. (F) TEM for EVs from M2-TAMs. Scale bars, 200 μm. (G−I) HepG2 cells cocultured with M2-TAMs were treated with sh-MIR17HG, and western blotting of TGF-β1 and BMP-7 pathway components and EMT genes was performed. PCR assays of stemness genes and migration (scale bars, 200 μm) and invasion (scale bars, 100 μm) abilities were performed. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.