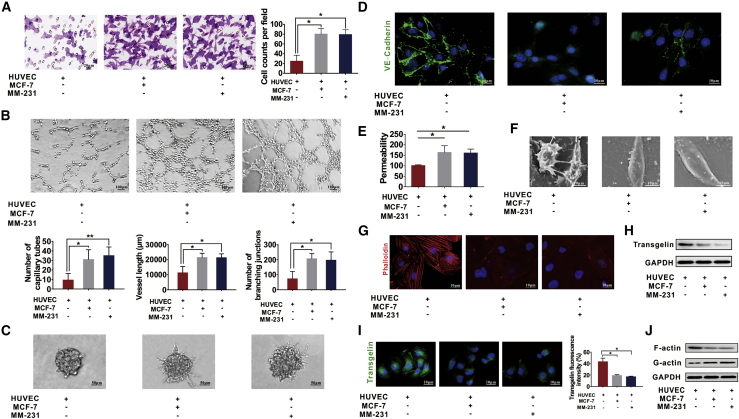
Figure 2.
HUVECs co-cultured with MCF or MM-231 cells exhibit abnormal vascularization and decreased transgelin (TAGLN) expression
(A) Transwell assays were performed to measure the migration ability of HUVECs co-cultured with MCF-7 or MM-231 cells. (B) HUVECs co-cultured with MCF-7 or MM-231 cells displayed a high number of capillary tubes, vessel length, and branching junctions in the tube formation assay. (C) Co-cultured HUVECs had increased spheroid sprouting, tube extension, and branching in the spheroid-based angiogenesis assay. (D) HUVECs co-cultured with MM-231 or MCF-7 cells had reduced expression of VE-cadherin, as shown in the IF assays. (E) Increased permeability was found in HUVECs co-cultured with MCF-7 or MM-231 cells examined a by rhodamine-dextran permeability assay. (F) Fewer cell junctions and increased cell pseudopodia were observed under a scanning electron microscope in HUVECs co-cultured with MCF-7 or MM-231 cells. (G) MCF-7/HUVEC or MM-231/HUVEC co-culture has an impaired cytoskeleton in the cytoskeleton staining assay. (H) Decreased TAGLN expression was observed in HUVECs co-cultured with BC cells in western blot assays. (I) Decreased TAGLN expression was observed in HUVECs co-cultured with BC cells in IF assays. (J) F-actin expression was decreased and G-actin expression was increased in HUVECs co-cultured with BC cells as detected by western blot assays. Results were repeated three times in independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.