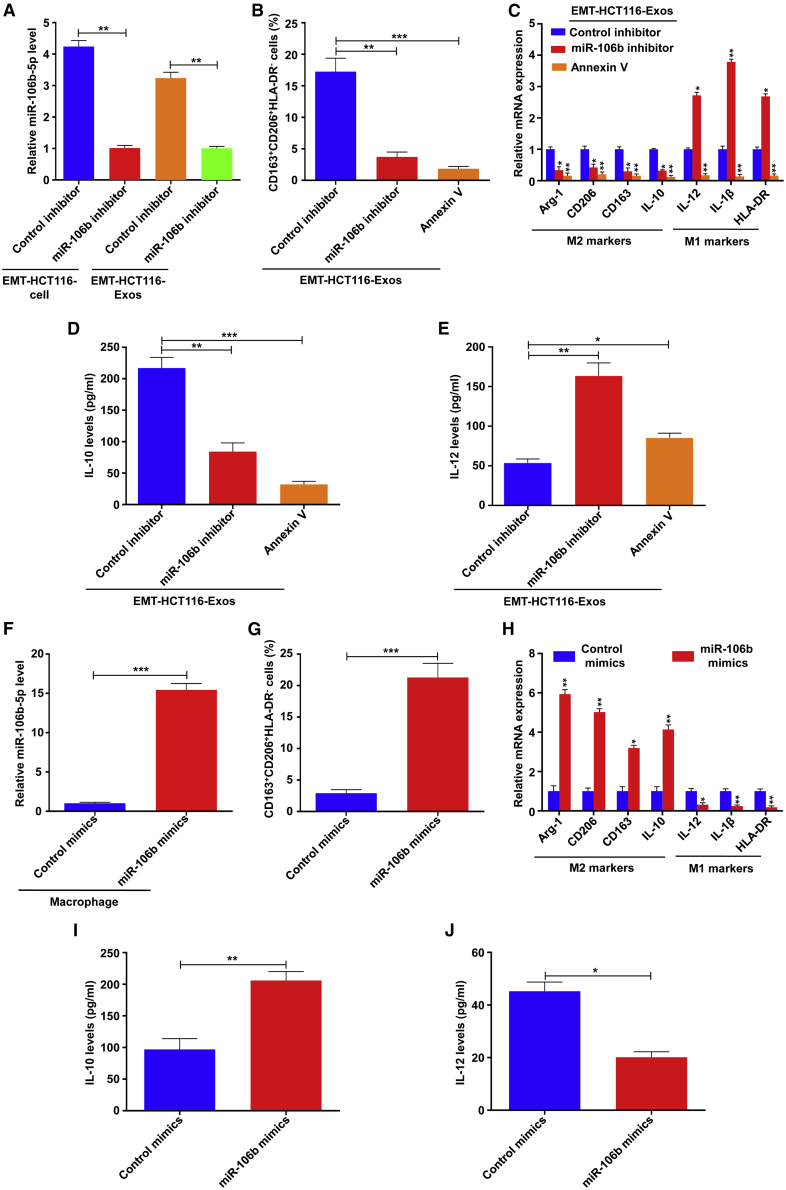
Figure 3.
EMT-Exos-derived miR-106b mediates M2 macrophage polarization
(A) qRT-PCR analysis of miR-106b-5p expression in cells and exosomes of EMT-HCT116 transfected by control inhibitor or miR-106b inhibitor. (B) Flow cytometry for analyzing the population of CD163highCD206highHLA-DRlow macrophages incubated with EMT-HCT116/mock-Exos, EMT-HCT116/miR-106b inhibitor-Exos, and EMT-HCT116-Exos + Annexin V groups. (C) qRT-PCR analyses of the macrophage-associated markers in macrophages cocultured with EMT-HCT116/mock-Exos, EMT-HCT116/miR-106b inhibitor-Exos, and EMT-HCT116-Exos + Annexin V groups. (D and E) ELISA for analyzing the secretion of IL-10 and IL-12 in macrophages incubated with EMT-HCT116/mock-Exos, EMT-HCT116/miR-106b inhibitor-Exos, and EMT-HCT116-Exos + Annexin V groups. (F) qRT-PCR analysis of miR-106b-5p expression in macrophages transfected by control mimics or miR-106b mimics. (G) Flow cytometry for analyzing the population of CD163highCD206highHLA-DRlow macrophages transfected by control mimics or miR-106b mimics. (H) qRT-PCR analyses of the macrophage-associated markers in macrophages transfected by control mimics or miR-106b mimics. (I and J) ELISA for analyzing the secretion of IL-10 and IL-12 in macrophages transfected by control mimics or miR-106b mimics. Experiments were performed in triplicates. Error bars, SEM. Statistical analysis was conducted using one-way ANOVA. p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.