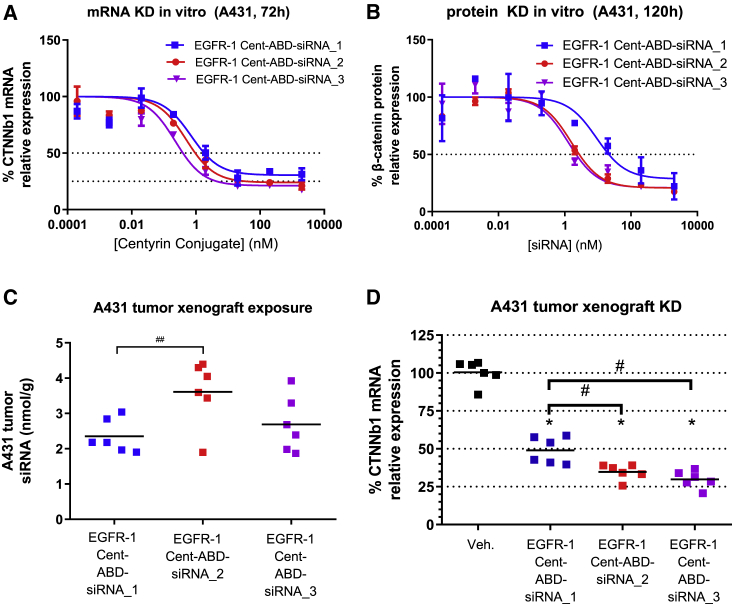
Figure 3.
mRNA knockdown (KD) potency of the same oligonucleotide sequence further optimized using changes in siRNA modification chemistry
(A) A431 cells were treated with three different EGFR-1-Cent-ABD-siRNA conjugates containing the same sequence but different chemical modifications or conjugation sites, as indicated in Table 1. (A and B) CTNNb1 mRNA expression after 72 h treatment determined by qRT-PCR (A) and β-catenin protein knockdown after 120 h determined by ELISA (B) are shown. Data represent average of two replicate samples at each dose. (C) Mice bearing A431 tumor xenografts were treated with a single dose of EGFR-1-Cent-siRNA containing various chemistries and conjugation sites (10 mpk by siRNA), and tumors were excised 72 h after dosing. siRNA levels were determined by stem-loop PCR, and (D) CTNNb1 mRNA expression was quantified by qRT-PCR. Chemistries used in siRNA_2 and siRNA_3 result in better tumor knockdown than siRNA_1. n = 6 mice per group. ∗p < 0.0001 versus vehicle. #p < 0.0001. ##p < 0.05.