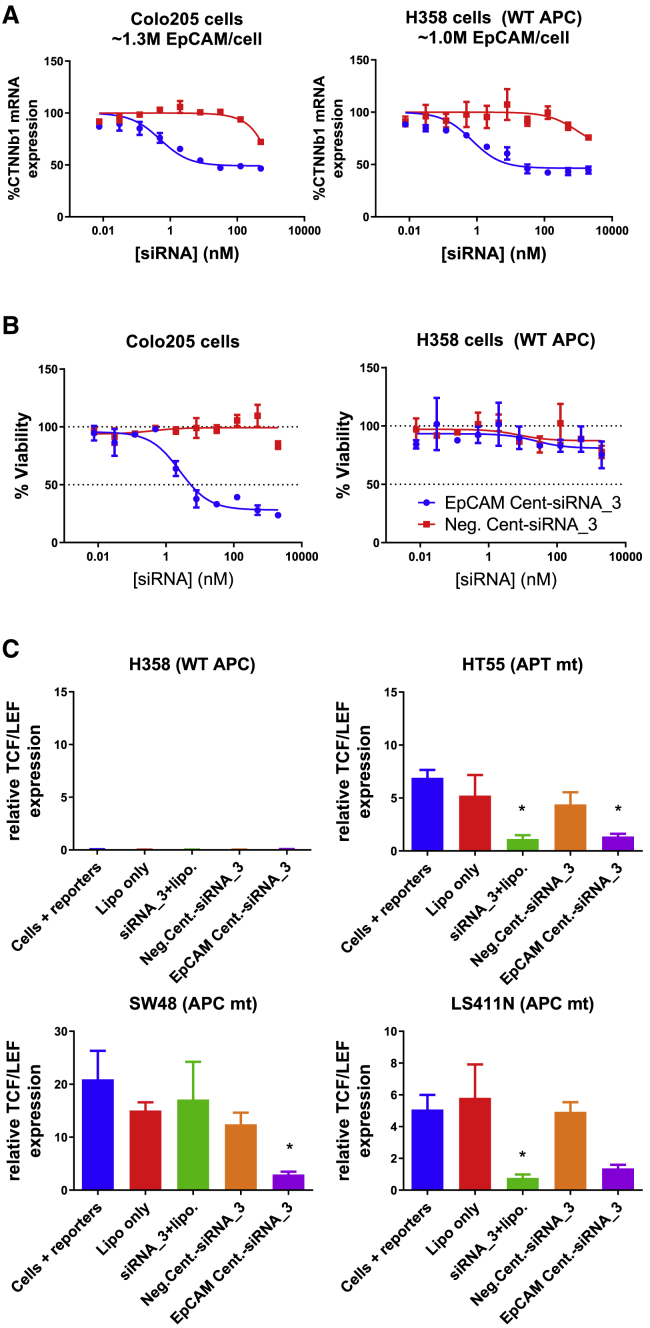
Figure 8.
Efficacy of EpCAM Centyrin-CTNNb1 siRNA conjugates in cells with APC mutations
(A) Colo205 or H358 cells were treated with a dose response of Centyrin-siRNA conjugates that bound to EpCAM (EpCAM Cent-siRNA_3) or that were nonbinding (neg. Cent-siRNA_3) for 72 h. Cells were treated at each concentration in duplicate. EpCAM Centyrin-siRNA conjugates induced potent reduction in CTNNb1 mRNA compared to nonbinding negative control Centyrin-siRNA conjugate in both Colo205 and H358 cells. (B) Colo205 or H358 cells were treated with a dose response of Centyrin-siRNA conjugates for 9 days (with media refreshed with fresh treatment after 5 days), and cell viability was assessed by CellTiterGlo. Cell viability was found to be significantly and selectively reduced in Colo205 cells (containing mtAPC) treated with EpCAM-Centyrin-siRNA conjugates but not in H358 cells, which are not reliant on CTNNb1 for growth as they do not have a mutation in either CTNNb1 or APC. (C) Downstream gene signaling, via a TCF/LEF reporter assay, was assessed in a panel of cells treated with reporters alone, lipofectamine, or transfected with CTNNb1 via lipofectamine or Centyrin-siRNA conjugates for 72 h. EpCAM Centyrin-siRNA conjugates reduced TCF/LEF activity in three cell lines containing mutant APC, to a level similar to that with lipofectamine transfection of free CTNNb1 siRNA. Data are plotted as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05 versus cells + reporters alone.