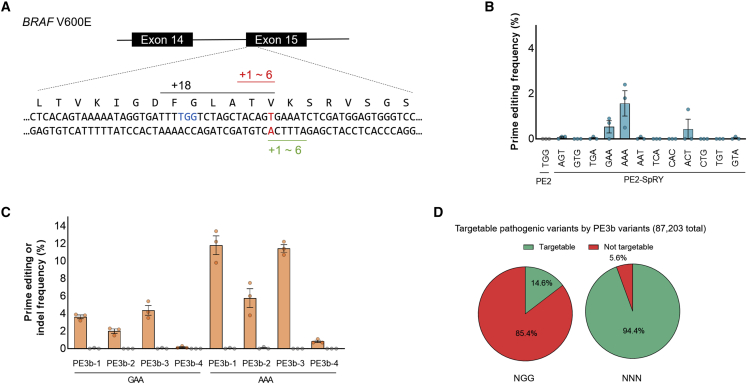
Figure 4.
The BRAF V600E mutation by the PE2-SpRY variant in HEK293T cells
(A) Schematic overview of prime editing for the BRAF V600E mutation. The target thymine nucleotide is highlighted in red, and the closest PAM sequence of wild-type PE2 (TGG) is indicated in blue, which can induce nick 18 nt away from that target thymine nucleotide. The 12 pegRNAs were designed to induce nicks of 1–6 nt in both directions from the target thymine by the PE2-SpRY variant. (B) Prime editing activities of PE2 and the PE2-SpRY variant at the BRAF V600E site. (C) Prime editing activity of the PE2-SpRY variant in PE3 and PE3b systems at the BRAF V600E site. The numerical values of the mutation frequencies are described in Table S1, and the information for pegRNAs is described in Table S2. Mean ± SEM of n = 3 independent biological replicates. (D) Comparison of prime editable pathogenic variants. Among 87,203 variants in the ClinVar database, targetable pathogenic variants using PE3b pegRNAs were analyzed by a computational pipeline, which was developed by Morris et al.27