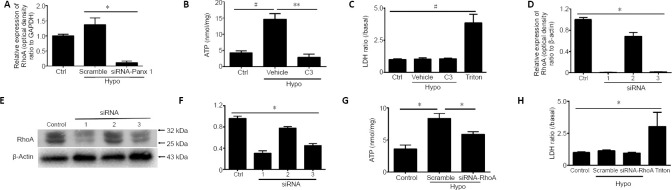
Figure 4.
Inhibition of RhoA activation reduced hypotonic solution-induced ATP release.
(A) Relative expression of RhoA upon treatment with isotonic (Ctrl) or hypotonic (Hypo) solution after transfection with scrambled and Panx 1 siRNA (3). (B) ATP release was assessed in Schwann cells treated with C3 transferase. Dimethyl sulfoxide at the same volume in isotonic solution was used as a control (Ctrl). (C) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release was assessed under the same conditions as ATP release in B. (D) RhoA mRNA levels in Schwann cells treated with scrambled siRNA (NC) and RhoA-siRNA (1–3). (E, F) Western blot images and mean analysis showing the levels of RhoA protein in Hepa 1–6 cells from the scrambled (Ctrl) and Panx 1-siRNA (1–3) groups. (G) ATP was assessed in scrambled siRNA- and RhoA-siRNA (3)-treated Schwann cells. Cells were treated with isotonic solution after transfection with scrambled siRNA as a control. (H) LDH release was assessed under the same conditions as ATP release. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (one-way analysis of variance or Student’s t-test). GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; Panx 1: pannexin 1; RhoA: Ras homolog family member A; siRNA: small interfering RNA; Vehicle: dimethyl sulfoxide.