Figure 1.
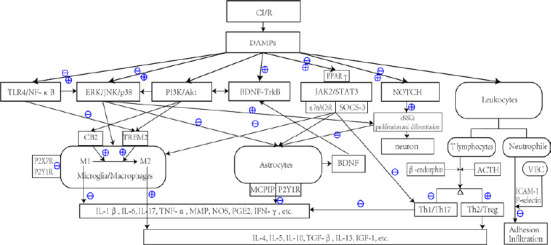
Inflammatory signal transmission related to acupuncture interventions after CI/R.
⊕ Indicates that acupuncture can promote and up-regulate pathways or the release of inflammatory mediators. ⊖ Indicates that acupuncture inhibits pathways or down-regulates the release of inflammatory mediators. ⊕/⊖ Indicates that acupuncture may exert biphasic regulation. For example, in the early stage of ischemia, acupuncture can up-regulate expression of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway, promote the proliferation and differentiation of glial cells and early scar formation, provide nutritional protection, and limit the inflammatory response. In the late stage, the TLR4/NF-κB pathway and TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and other inflammatory cytokines are inhibited, which significantly improves nerve injury and reduces the inflammatory response. Acupuncture also exerts biphasic regulatory effects on microglia, which not only increases the phagocytic function of microglia in the ischemic penumbra, but also downregulates the inflammatory damage caused by the over activation of microglia. ACTH: Adreno-corticotropic hormone; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CB2: type II cannabinoid receptor; CI/R: cerebral infarction/reperfusion; DAMP: damage-associated molecular pattern; eNSC: endogenous neural stem cell; ERK: extracellular regulated protein kinase; ICAM-1: intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1; IFN-γ: interferon-γ; IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor-1; IL: interleukin; JAK2: Janus kinase 2; JNK: c-jun N-terminal kinase; MCPIP: monocyte chemotactic protein-induced protein; MMP: matrix metalloproteinase; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-B; NOS: nitric oxide synthase; P2X7R: P2X purinoceptor 7; P2Y1R: P2Y purinoceptor 1; P2Y7R: P2Y purinoceptor 7; PGE2: prostaglandin E2; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; SOCS-3: suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-β; TLR4: Toll like receptor 4; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; TREM2: triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2; VEC: vascular endothelial cell; α7nAChR: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.
