Figure 2.
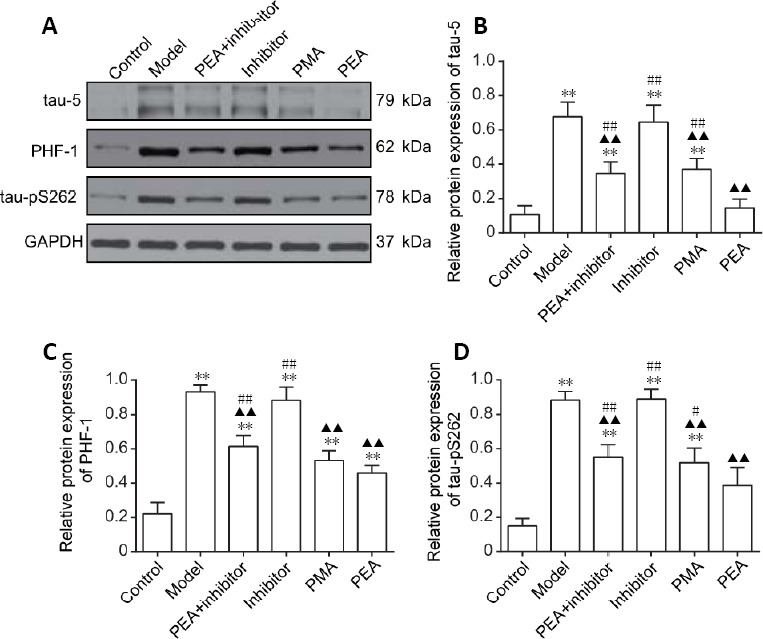
Effects of acupuncture treatment on the expression of phosphorylated tau in the dorsal raphe nucleus in the rat model of D-galactose-induced aging.
(A) The protein expression levels of tau-5, PHF-1 and tau-pS262 in the dorsal raphe nucleus were detected using western blot assay. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B–D) Quantitative results for tau-5 (B), PHF-1 (C) and tau-pS262 (D) expression (optical density ratio to GAPDH). The data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 6). **P < 0.01, vs. control group; ▲▲P < 0.01, vs. model group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, vs. PEA group (one-way analysis of variance followed by the least significant difference test). Control: Normal; Model: D-galactose-induced aging; PEA + inhibitor: D-galactose-induced aging + preventive electroacupuncture + 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (an inhibitor of DNA methyltransferase); Inhibitor: D-galactose-induced aging + 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine; PMA: D-galactose-induced aging + preventive manual acupuncture; PEA: D-galactose-induced aging + preventive electroacupuncture. GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PHF-1: paired helical filament 1.
