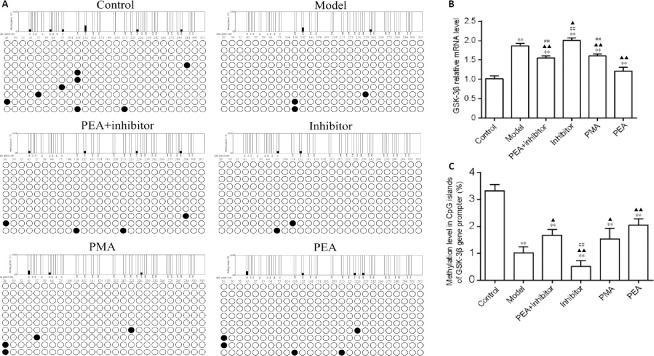
Figure 4.
Effects of acupuncture treatment on cytosine methylation in the promoter region of the GSK-3β gene and GSK-3β mRNA levels in the dorsal raphe nucleus in the rat model of D-galactose-induced aging.
(A) The methylation level in the promoter region of GSK-3β was detected using bisulfite sequencing-polymerase chain reaction. (B) Quantitation of GSK-3β mRNA levels, detected using real-time polymerase chain reaction. (C) Quantitation of methylation levels in CpG islands of the GSK-3β gene promoter. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). **P < 0.01, vs. control group; ▲P < 0.05, ▲▲P < 0.01, vs. model group; ##P < 0.01, vs. PEA group (one-way analysis of variance followed by the least significant difference test). Control: Normal; Model: D-galactose-induced aging; PEA + inhibitor: D-galactose-induced aging + preventive electroacupuncture + 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine; Inhibitor: D-galactose-induced aging + 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine; PMA: D-galactose-induced aging + preventive manual acupuncture; PEA: D-galactose-induced aging + preventive electroacupuncture. GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GSK-3β: glycogen synthase kinase-3β.