Inhibition of AspH by 2OG derivatives.
| 2OG derivativea | IC50b,c [μM] | 2OG derivativea | IC50b,c [μM] | 2OG derivativea | IC50b,c [μM] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
|
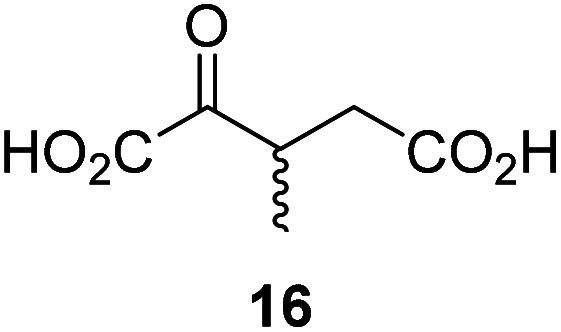
Inactive | 12 |
|
0.61 ± 0.09 | 23 |
|
12.9 ± 1.3 |
| 2 |
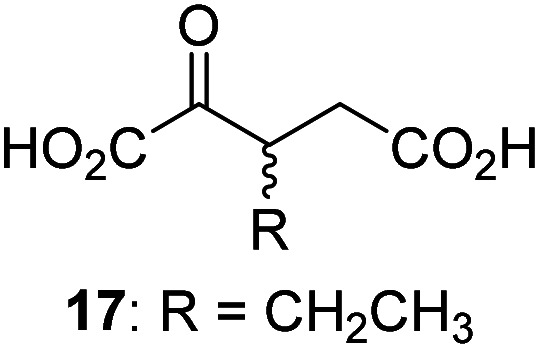
|
1.2 ± 0.5 | 13 |
|
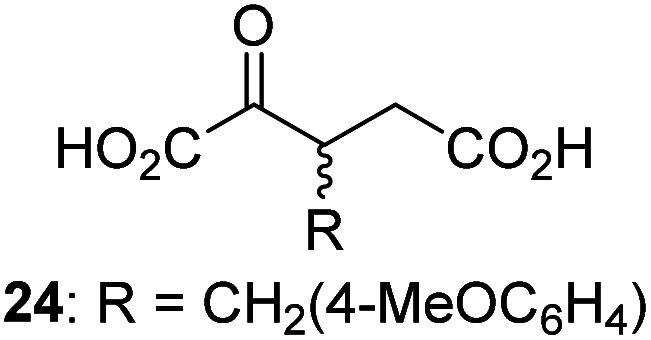
0.47 ± 0.08 | 24 |
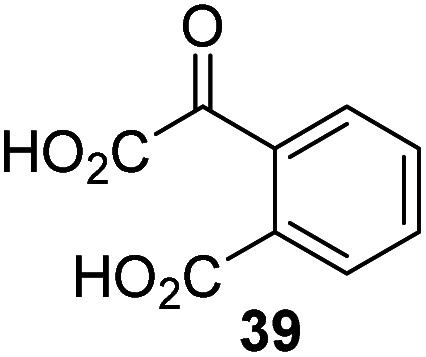
|
Inactive |
| 3 |
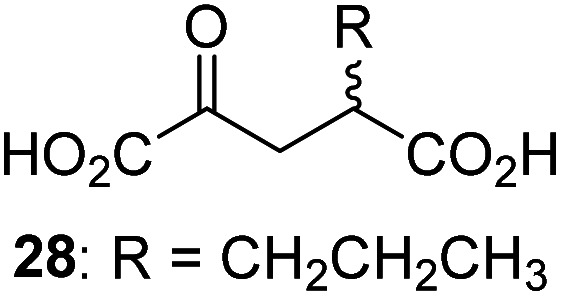
|
5.7 ± 1.1 | 14 |
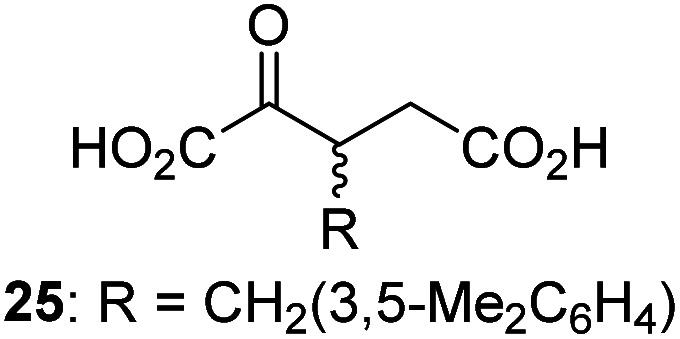
|
0.51 ± 0.12 | 25 |
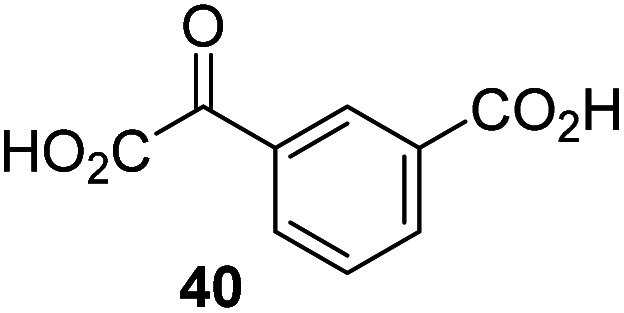
|
Inactive |
| 4 |
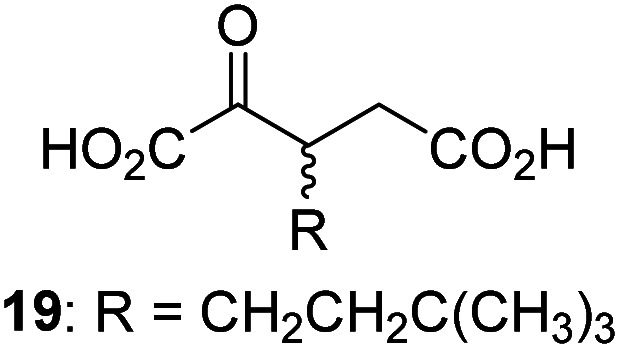
|
48.2 ± 13.1 | 15 |
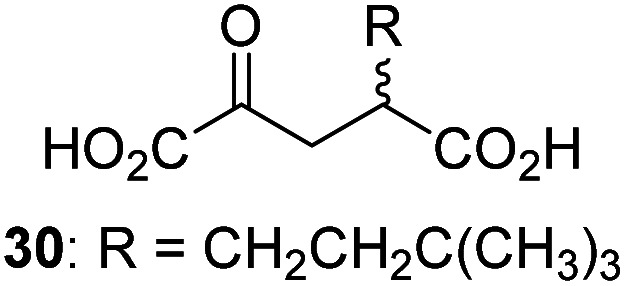
|
0.70 ± 0.11 | 26 |
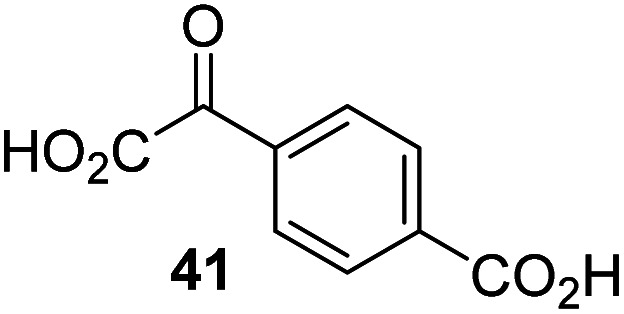
|
Inactive |
| 5 |
|
6.8 ± 0.9 | 16 |
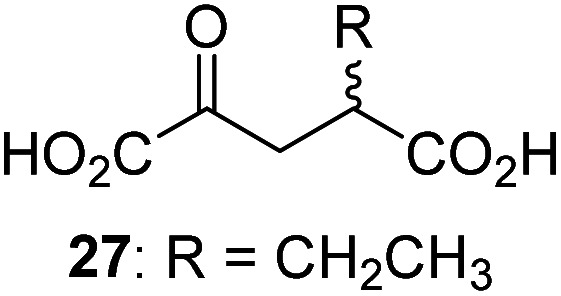
|
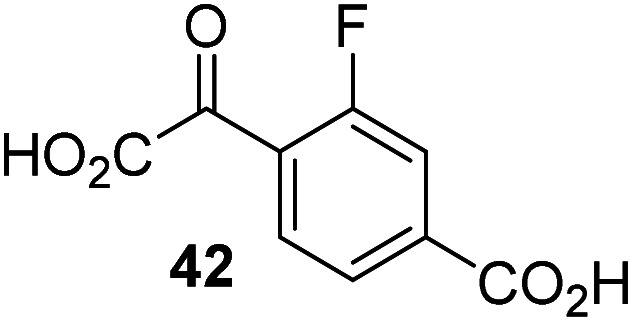
0.25 ± 0.05 | 27 |
|
Inactive |
| 6 |
|
1.6 ± 0.3 | 17 |
|
0.43 ± 0.05 | 28 |
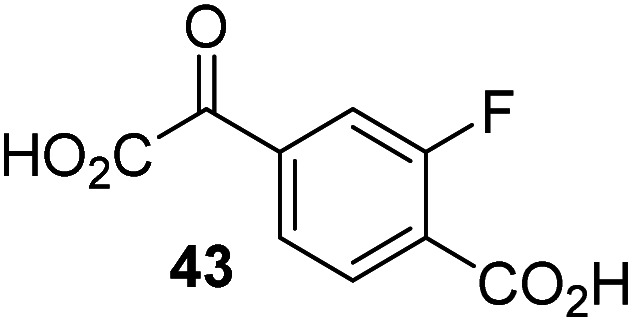
|
Inactive |
| 7 |
|
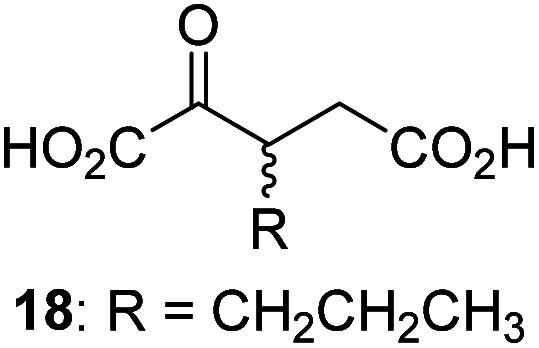
2.6 ± 0.8 | 18 |
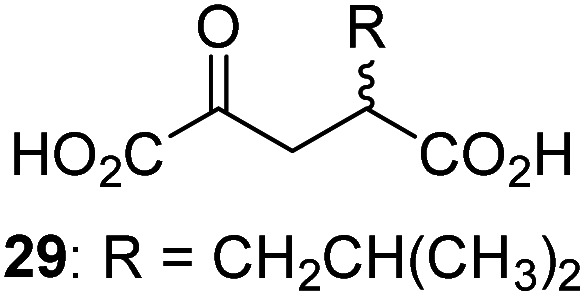
|
0.17 ± 0.03 | 29 |
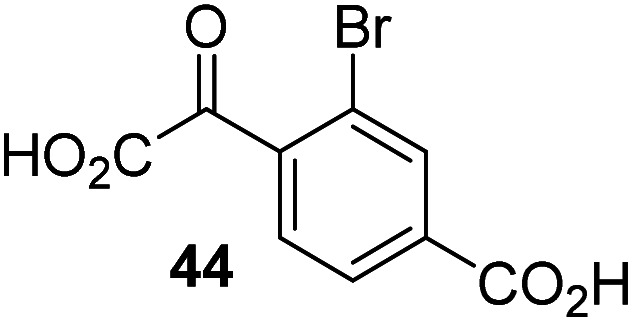
|
Inactive |
| 8 |
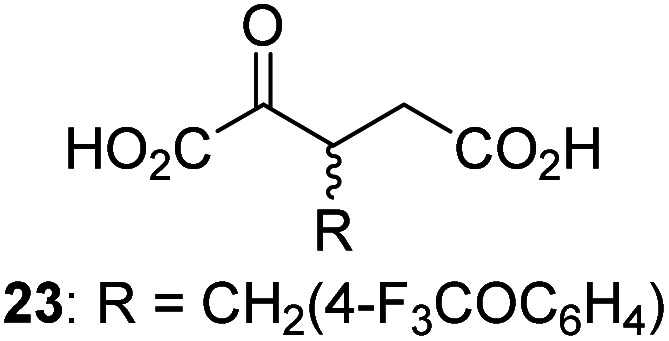
|
6.3 ± 2.6 | 19 |
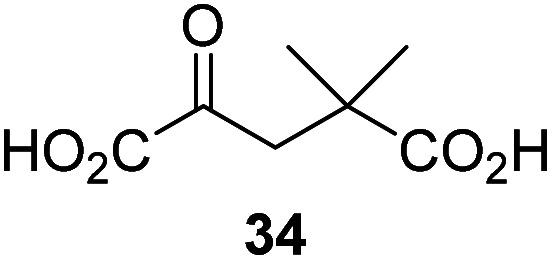
|
0.3 ± 0.1 | 30 |
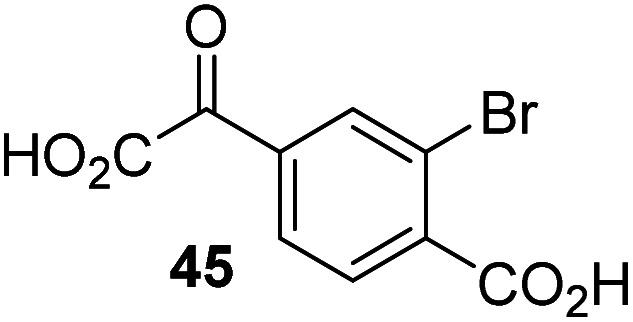
|
Inactive |
| 9 |
|
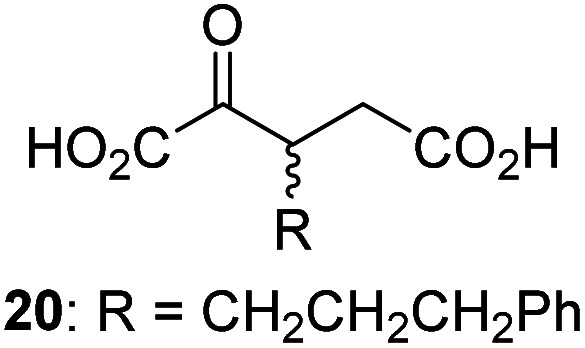
3.6 ± 1.4 | 20d |
|
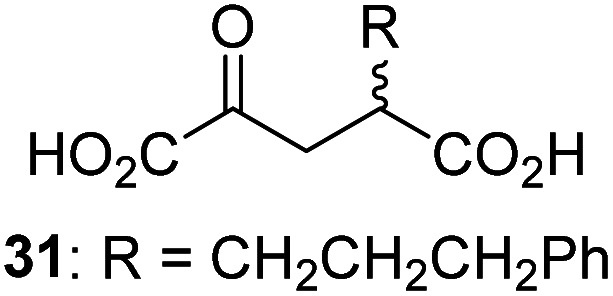
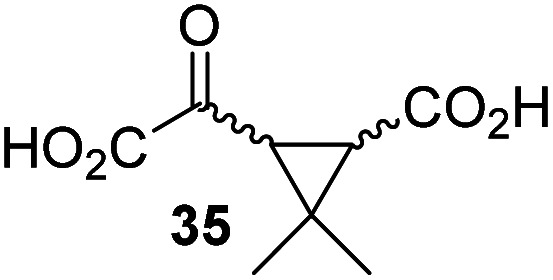
5.2 ± 1.7 | 31 |
|
Inactive |
| 10 |
|
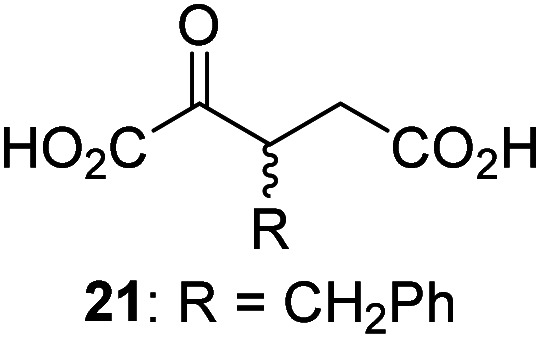
4.7 ± 0.2 | 21e |
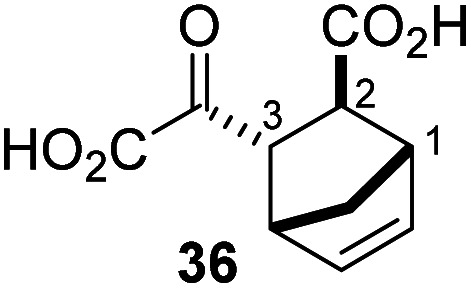
|
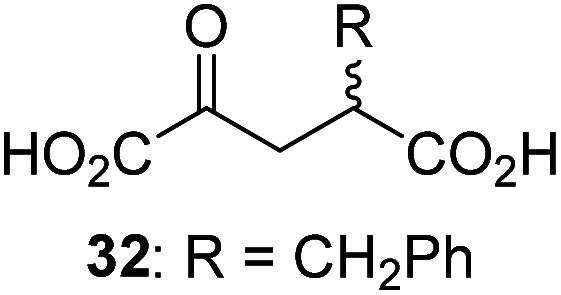
19.3 ± 1.6 | 32 |
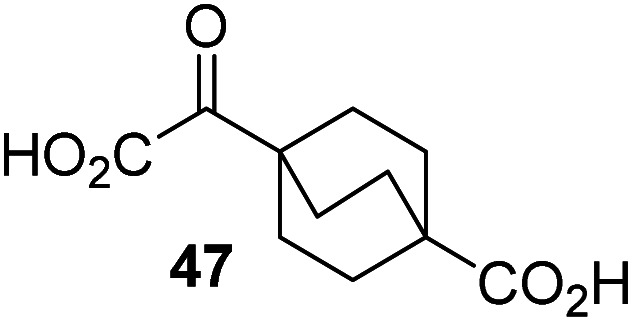
|
Inactive |
| 11 |
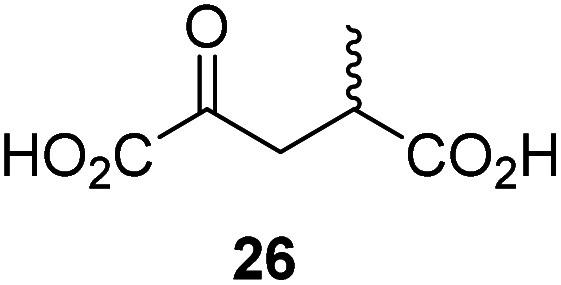
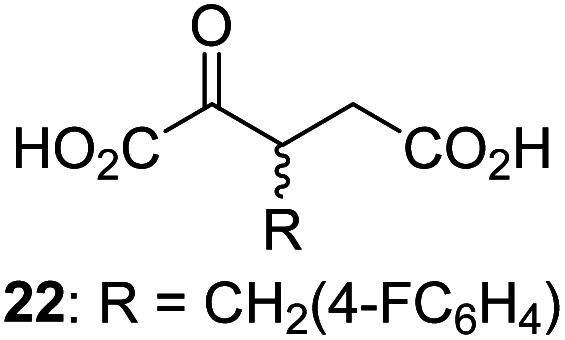
|
Inactive | 22 |
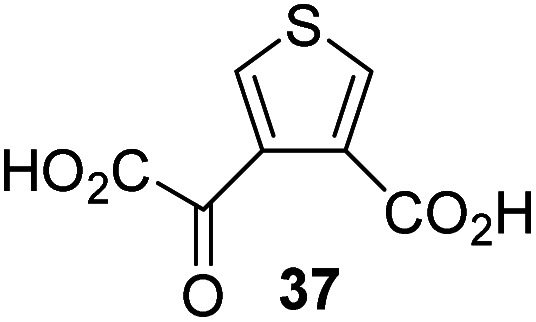
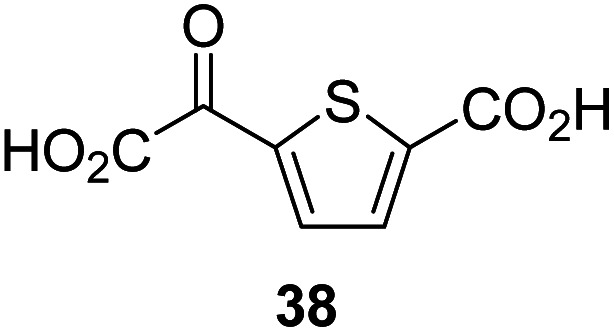
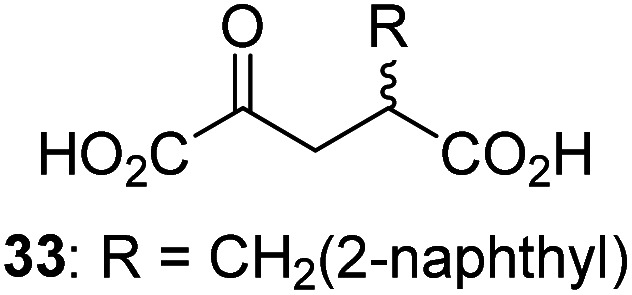
|
Inactive | 33 |
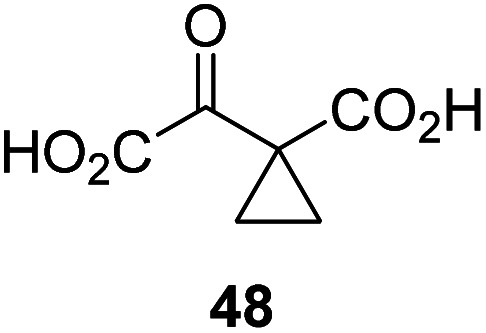
|
3.3 ± 1.0 |
All chiral 2OG derivatives were prepared as racemic mixtures.
Mean of three independent runs (n = 3; mean ± SD). AspH inhibition assays were performed as described in the ESI using 50 nM His6-AspH315–758 and 1.0 μM hFX-CP101–119 (ESI Fig. S1d) as a substrate.
2OG derivatives were termed inactive when the IC50-values were >50 μM. The AspH inhibition assays were of good quality which high S/N ratios and Z′-factors40 (>0.5 for each plate) indicate (ESI Fig. S3).
Mixture of racemic diastereomers, dr (cis : trans) = 2.5 : 1.
(±)-(2-Exo,3-endo)-diastereomer.
