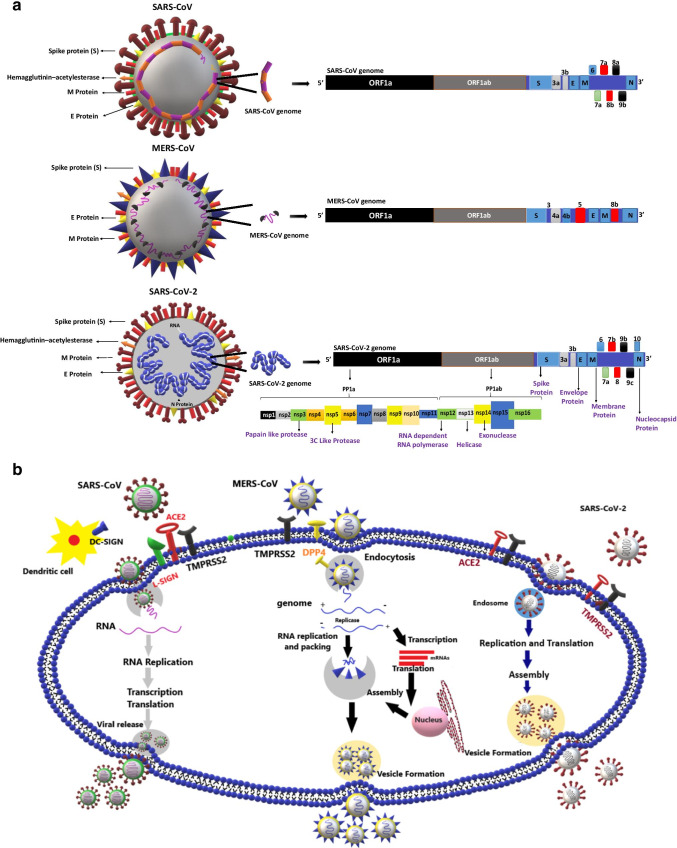
Fig. 1.
Genome organization of coronaviruses and variations in their mode of entry into human cells: a Structural representation and genome organization of SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2: SARS-CoV-2 genome encodes four major proteins viz., spike (S) protein, the nucleocapsid (N) protein, the membrane (M) protein, and the envelope (E) protein. Total six open reading frames (ORFs), ORF3a, ORF6, ORF7a, ORF7b, ORF8, ORF10, and the polyprotein ORF1ab encodes several enzymatic proteins for the effective viral invasion of the host cells. b Host cell receptors and replication mechanism of SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-COV-2: the spike protein of the CoVs interacts with receptors on the host cell to make its entry. ACE-2 serves as a receptor for SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. DC-SIGN and L-SIGN serve as co-receptors for SARS-CoV. DPP4 serves as a receptor for MERS-CoV. CoVs replicate in the host causing cellular damage leading to further complications