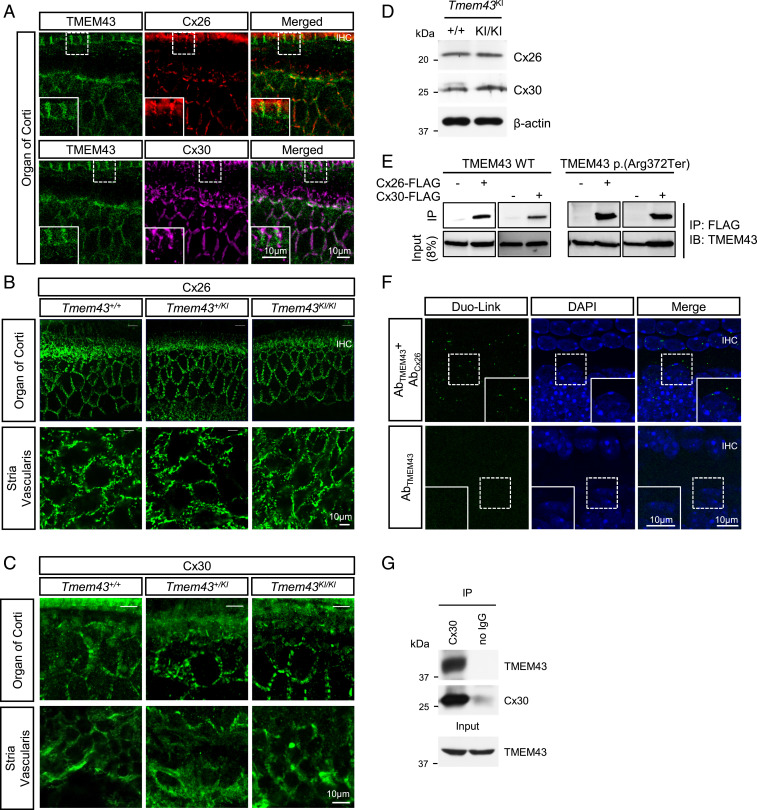
Fig. 6.
TMEM43 interacts with Cx26 and Cx30 gap junction channels. (A) Immunohistochemistry data showing TMEM43 expression with Cx26 and Cx30 in GLSs (P20). Merged images are shown in Bottom. TMEM43, green; Cx26, red; Cx30, magenta; DAPI, blue. (B) Confocal micrographs of Cx26 expression in the organ of Corti (Top) and Stria Vascularis (Bottom) of Tmem43+/+, Tmem43+/KI, and Tmem43KI/KI (5 mo). (C) Confocal micrographs of Cx30 expression in the organ of Corti (Top) and Stria Vascularis (Bottom) of Tmem43+/+, Tmem43+/KI, and Tmem43KI/KI (7 mo). There was no difference among the genotypes. (D) Western blot result from cochlea tissue lysates of Tmem43+/+ and Tmem43KI/KI mice (p6), blotted with anti-Cx26 and anti-Cx30. (E) Co-IP data showing that both TMEM43 WT and TMEM43-p.(Arg372Ter) are immuno-pulled down with Cx26 and Cx30 in in vitro. (F) Duolink PLA with anti-TMEM43 and anti-Cx26 (Top). Duolink PLA signal was amplified as a red fluorescent, indicative of close proximity of TMEM43 and Cx-26. Red signal was pseudo colored as green for better data display. Lower is a negative control data without Cx26 antibody. (G) Co-IP data using cochlea tissue (p6). Protein lysate was pulled down with Cx30 antibody and blotted with anti-TMEM43.