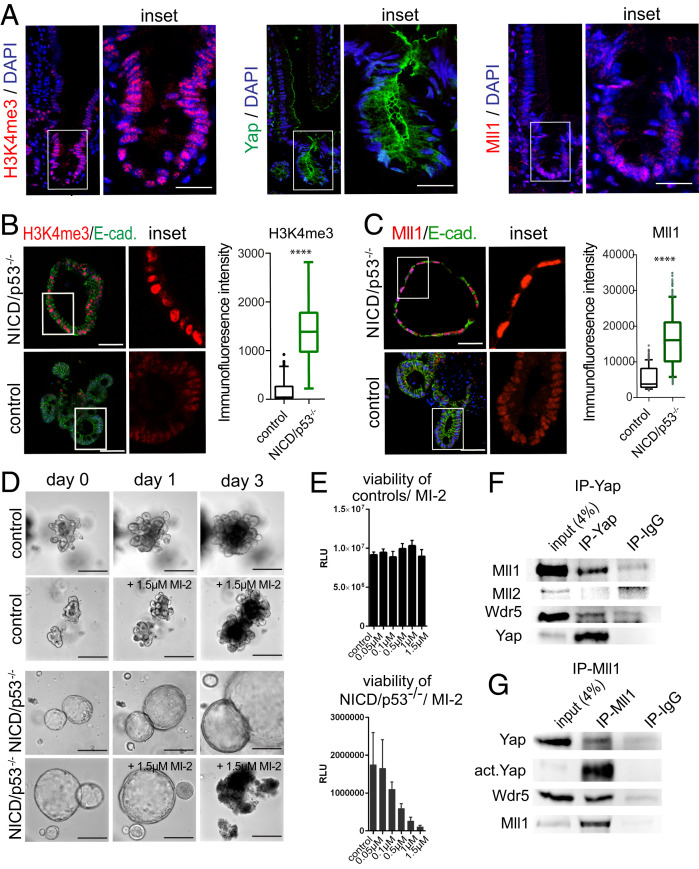
Fig. 4.
Menin-Mll1/Mll2 interaction mediates H3K4me3, cell proliferation, and viability of NICD/p53−/− organoids. (A) Immunofluorescence staining of small intestinal crypt for H3K4me3 (Left), Yap (Middle), and Mll1 (Right). (Scale bar, 30 µm.) (B) Immunofluorescence staining of NICD/p53−/− (Upper) and control organoids (Lower) for H3K4me3 (red) and E-cadherin (green). (Scale bar, 50 µm.) Magnifications of Insets on the Right. Quantification of staining intensity on the Far Right. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of NICD/p53−/− (Upper) and control organoids (Lower) for Mll1 (red), E-cadherin (green), and DAPI (Scale bar, 50 µm.); Insets are enlarged on the Right. Quantification of staining intensity on the Far Right. (***P ≤ 0.0001.) (D) Brightfield images of individual tracked control (Upper) and NICD/p53−/− organoids (Lower) either untreated or in response to MI-2 treatment. (Scale bar, 250 µm.) (E) Concentration-dependent viability of control (Upper) and NICD/p53−/− organoids (Lower) treated with increasing concentrations of MI-2. (F) Coimmunoprecipitation of endogenous proteins from NICD/p53−/− organoids; Yap coprecipitates with Mll1 and Wdr5, but not with Mll2. (G) Coimmunoprecipitation of endogenous Mll1 with Yap and Wdr5 from lysates of NICD/p53−/− organoids.