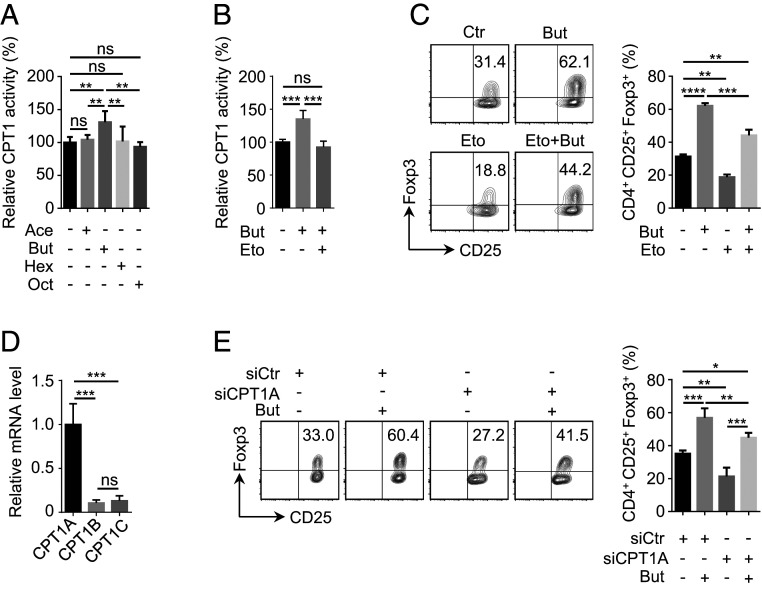
Fig. 2.
Regulation of CPT1A activity contributes to enhanced iTreg cell differentiation by butyrate. (A and B) Examination of impact from different types of fatty acids (FAs) on CPT1 activity. In the presence of FAs at the same concentration (125 μM), including acetate (Ace), butyrate (But), hexanoate (Hex), or octanate (Oct), naive CD4+ T cells were cultured under iTreg-polarization condition as described in Fig. 1A for 24 h and lysed for the assessment of CPT1 activity (A). Etomoxir (Eto) (5 μM), a well-documented CPT1 inhibitor (26), was added together with But for the evaluation of But-dependent up-regulation in CPT1 activity (B). (C) Analysis of iTreg generation upon the inhibition of CPT1. In the presence of But or/and Eto, naive CD4+ T cells were cultured under iTreg-polarization condition as described in Fig. 1A for 72 h. iTreg cells positive for CD4, CD25, and Foxp3 were analyzed by flow cytometry (Left) and quantified accordingly (Right). (D) Assay for mRNA levels of distinct CPT1 isoforms. RT-qPCR was performed using iTreg cells cultured as described in Fig. 1A for 24 h. (E) Evaluation of iTreg differentiation for CPT1A-depleted cells. Naive CD4+ T cells isolated from mice were transfected with siRNA against CPT1A. Following 4-h incubation, cells were replaced into fresh medium supplemented with or without But and kept under iTreg-polarization condition as described in Fig. 1A for 72 h. iTreg cells positive for CD4, CD25, and Foxp3 were analyzed by flow cytometry (Left) and quantified accordingly (Right). Data represent mean ± SD (n = 3) of three independent experiments, with significance determined by one-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; ns, nonsignificant.