Optimization of the oxidative decarboxylation of dipeptides.
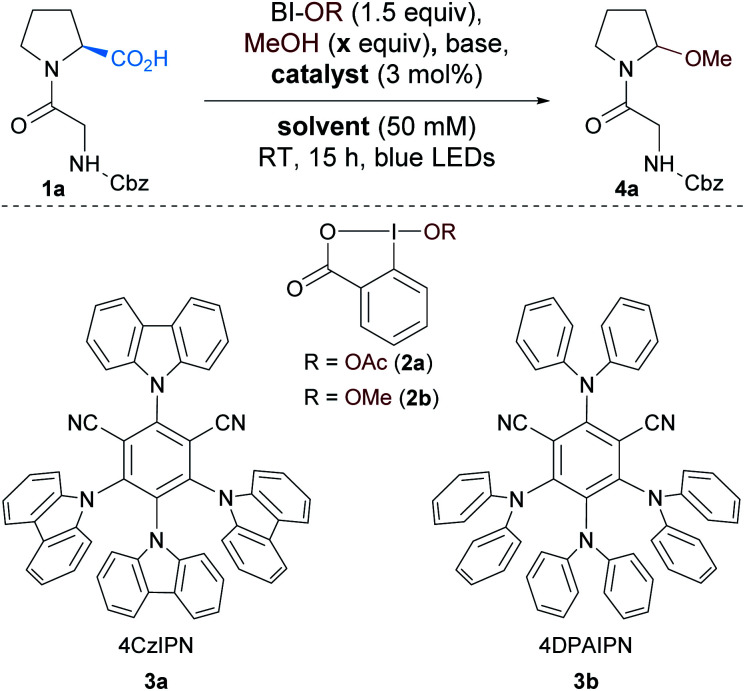
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Solvent | Catalyst | x | Base (2 equiv.) | HPLC yielda (%) |
| 1b | DMF | 4CzIPN (3a) | 50 | K2HPO4 | 46 (18)c |
| 2b | DMF | Ru(bpy)3Cl2 | 50 | K2HPO4 | 59 |
| 3b | DMF | Ru(bpy)3Cl2 | 10 | K2HPO4 | 78 |
| 4 | DMF | Ru(bpy)3Cl2 | 10 | K2HPO4 | 82 |
| 5 | DMF | Ru(bpy)3Cl2 | 5 | K2HPO4 | >95 |
| 6 | DMF | Ru(bpy)3Cl2 | 2 | K2HPO4 | >95 |
| 7 | DMF | Eosin Y | 5 | K2HPO4 | 17 |
| 8d | DMF | Rhodamine B | 5 | K2HPO4 | 27 |
| 9d | DMF | Rose bengal | 5 | K2HPO4 | 35 |
| 10d | DMF | 4DPAIPN (3b) | 5 | K2HPO4 | 45 |
| 11 | MeCN | Ru(bpy)3Cl2 | 5 | K2HPO4 | >95 |
| 12 | MeCN | Ru(bpy) 3 Cl 2 | 5 | None | >95 (68) c |
| 13 | DCE | Ru(bpy) 3 Cl 2 | 5 | None | >95 |
| 14 e | MeCN | Ru(bpy) 3 Cl 2 | 0 | None | >95 (75) c |
Ratio of integration at 214 nm by RP-HPLC.
Concentration 10 mM.
Isolated yield on 0.3 mmol.
Green LEDs.
BI-OMe (2b) instead of BI-OAc (2a).
