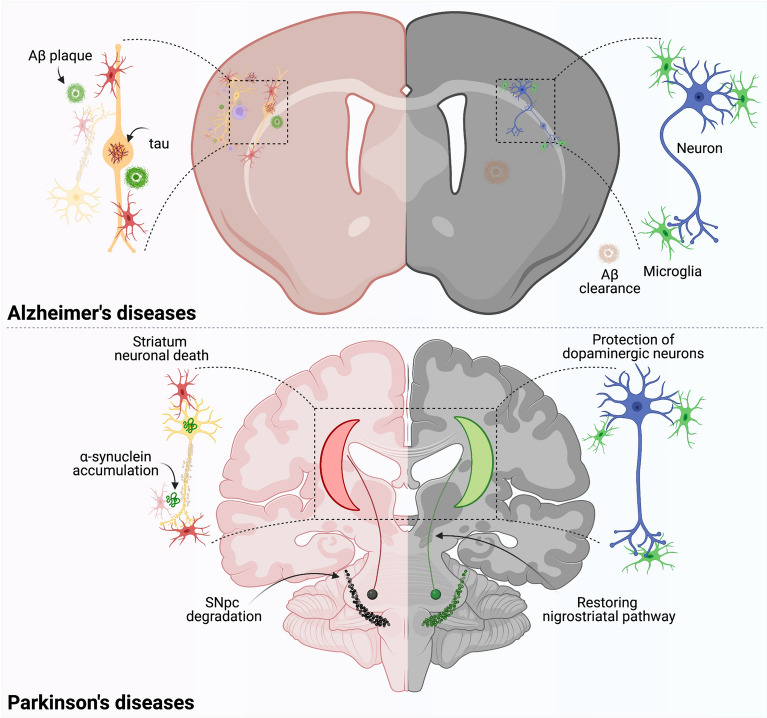
Fig. 3.
Immune transformation in neurodegenerative disorders. Pathogenic changes seen in the brains of AD include accumulation of intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles of Tau and extracellular Aβ plaques. These induce activation of CNS resident microglia and astrocytes leading to neuroinflammation (top left). In contrast, transformation of an inflammatory microglia by medicines or immune modulation leads to neuronal protection and maintenance of CNS homeostasis (top right). Similarly in PD, aggregated self-protein α-synuclein activates microglia leading to neuronal damage within the substantia nigra pars compacta along with their connections into the striatum; brain subregions responsible for coordinate movement (bottom left). However, brain homeostasis achieved through neuroprotection (bottom right) can affect clinical improvements