Abstract
Background
Breast cancer (BC) is the common primary tumor among females. Hence, there is an urgent need to improve the early prediction and diagnosis of BC. For that reason, the object of the current study is to analyze the expression levels of miRNA-373 and its target genes including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and cyclin D1 in women with BC.
Results
Upregulation of miRNA-373 and its target genes was observed in BC patients followed by patients with benign breast lesions compared to downregulation in controls. There was a significant association between the expression level of miRNA-373 and all clinical features. The same associations were observed between its target genes and all clinico-pathological features except hormonal status. The correlation between miRNA-373 and both genes was significant.
Conclusions
Our results prove that miRNA-373, as an oncomir, would be a vital biomarker for BC diagnosis and prognosis by targeting both VEGF and cyclin D1.
Keywords: Breast cancer, Clinico-pathological characteristics, VEGF, Cyclin D1, Diagnosis, MicroRNA
Background
Breast cancer (BC) is the most frequently diagnosed malignant tumor in women and the principal cause of female cancer-related mortality [1]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to assess specific biomarkers of diagnostic value in order to decrease cancer-related deaths [2].
The cell cycle progression plays a crucial role in cell proliferation, and its deregulation is the most important cause of tumorigenesis [3–5]. Also, vascularization of tumor cells is pivotal in cancer initiation and progression [6]. Normal cells have a limited capability for cell division, once reaching an optimal cell density within a tissue, they will stop from proliferation, block at the gap 0 (G0) phase of the cycle, and still inactive, and this performance is owing to the response to the environmental growth inhibitory effects [7]. This cell cycle arrest mechanism, which physiologically adapted, is abnormal in tumor cells [8, 9]. In BC, anomalies of the cell cycle are frequently noted, including loss of function of retinoblastoma (Rb), decreased abundance of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors like p21 and p27, and overexpression of D and E type cyclins [10, 11].
Angiogenesis is a physiological process that is the creation of novel capillaries from pre-existing blood vessels [12, 13]. The process of angiogenesis is critical not only for normal processes, but also for pathophysiological alterations like cancer development [14]. In cancer progression, the unbalance between pro- and anti-angiogenic factors causes abnormal homeostasis of the blood vessels [15]. However, some types of cancer benefit from anti-angiogenic therapies while others resist treatment, which may be due to the variation of gene expression as reported earlier [6].
miRNAs play critical roles in biological processes like cell cycle regulation, differentiation, migration, and tumor progression [16]. miRNAs, a new category of small non-coding RNA molecules, regulate the expression of their targeted genes post-transcriptionally and affect various important pathways involved in tumorigenesis [17]. A human embryonic stem cell (ESC)-specific miRNA, miRNA-373, has new tumorigenic influences through mediating the proliferation and tumorigenesis of primary human cells that harbor oncogenic mediators involving rat sarcoma (RAS) and wild-type p53 [18–20]. It could be a potential biomarker for breast cancer patients due to its differential expression and close relation with tumor invasion and metastasis in cancer cells and tissue reports [21, 22].
According to the miRTarBase (http://miRTarBase.mbc.nctu.edu.tw/), a database that covers miRNA-target interactions (MTIs), miRNA-373 targets many genes, among them are cyclin D1 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Cyclin D1 is the protein product of the CCND1 gene, which is found on chromosome 11q13 [23]. It is the well-distinguished cell cycle regulator through binding with cdk4/6 creating a cyclin D1-cdk4/6 complex [24]. In the course of the cell cycle progression, this associate stimulates the phosphorylation and deactivation of the Rb, causing transporting cells from gap 1 (G1) phase to synthesis (S) phase [25]. When cyclin D1 deregulated (overexpressed and accumulated), it becomes an oncogene in several tumors including BC and causes several genetic alterations in regulatory proteins of the cell cycle [25]. In addition to its CDK-dependent functions, it may stimulate ER-mediated transcription, independent of estrogen, and in this way altering the estrogen response [26].
VEGF, pro-angiogenic factor and prognostic marker with numerous types of cancer including BC [27], plays a vital role in tumor progression and metastasis [28]. In BC, it plays a key role in the progression of the disease through its influences on tumor angiogenesis and through its autocrine functions in breast cancer cell migration and invasion [29].
The goal of the current study is to examine the expression levels of miRNA-373 and VEGF, and cyclin D1 in Egyptian breast cancer patients as minimal noninvasive molecular markers for diagnostic purposes, and their impact on clinical characteristics of breast cancer. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the effect of dysregulation of miRNA-373 on the expression levels of its target genes including VEGF as well as cyclin D1 in breast cancer patients.
Methods
Study design and sample processing
A total of 321 participants were enrolled in the current study; they were divided into newly diagnosed breast cancer patients (n=196), patients with benign breast lesions (n=76), and healthy volunteers as the control group (n=49). The inclusion criteria included those who have not received any treatment modalities or have any other malignancies. The exclusion criteria included patients with invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). The staging and grading classifications of BC patients [30] were obtained from their clinical sheets.
After obtaining ethical approval from the Medical Ethical Committee, and signing the informed consent, 5 ml blood was withdrawn from the enrolled individuals and divided into two tubes: one with polymer gel and clot activator that allow for further separation of the serum and stored in −80 °C for further processing to separate miRNA, and the other tube containing ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) for further processing of RNA separation and genes expression detection.
miRNA and RNA isolation from human serum samples
The miRNA and mRNA isolations were performed following the instructions in the manual manufacturer’s protocols of the Qiagen miRNeasy Mini Kit (Cat number# 217004, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and QIAamp RNA Blood Mini kit protocol (Cat no # 52304 Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), respectively. All preparations and handling of RNA were performed in a laminar flow hood, under RNase-free conditions. The concentration and purity of the resulted miRNA and RNA were evaluated using the Nanodrop spectrophotometer (Quawell, Q-500, Quawell Technology Inc., San Jose, CA), and then stored at −80 °C until used.
cDNA synthesis
Reverse transcription of miRNA and RNA was performed by the MiScript II reverse transcription kit (Cat number # 218160, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manual manufacturer’s protocol in a final reaction volume of 20μl. The concentration and the purity of cDNA were measured by the Nanodrop spectrophotometer and then stored at −20 °C until used.
Detection of miRNA and mRNA expression level by QPCR
QPCR was carried out for the detection of miRNA expression using the MiScript SYBR Green PCR primer assay (Cat number 218300, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany): miR-373 (Hs_miR-373, MS00031815), and endogenous control assay for RNU6B (Hs_RNU-2_11, MS00033740). The reaction mixture (25μl) included 12.5μl 2× QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR Master Mix, 2.5μl 10× miScript Universal Primer, 2.5μl 10× miScript Primer Assay, 4μl RNase-free water, and 2μl cDNA. For mRNA, the QuantiTect primer assays (product number 249900, Qiagen, USA) for VEGF primer assay (Hs_VEGF_1_SG, QT00013783) and cyclin D1 primer assay (Hs_CCND1_1_SG, QT00495285) and the endogenous control assay GAPDH (Hs_GAPDH_1_SG, QT00079247). The reaction mixture (25μl) included 12.5μl 2× QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR Master Mix, 2.5μl 10× QuantiTect Primer, 4μl RNase-free water, and 2μl cDNA. The PCR was performed in the QPCR system (Max3005P QPCR system; Stratagene, Agilent Technologies, CA) as follows: initial denaturation at 95°C for 15 min then 94°C for 15 s, 55°C for 30 s, and 70°C for 30 s for 40 cycles. The relative expression levels of the investigated miR-373, VEGF, and cyclin D1 were evaluated using the 2−ΔΔCt method [31]. The cycle threshold (Ct) value is the number of qPCR cycles required for the fluorescent signal to cross a specified value. ΔCt was calculated by subtracting the Ct values of RNU6B from Ct miR-373 for the detection of its expression and subtracting the Ct values of GAPDH from Ct VEGF and cyclin D1 in case of gene expression analysis. ΔΔCt was calculated by subtracting the ΔCt of the control samples from the ΔCt of the cancer samples.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were carried out using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) software version 16.0, and P values were two-tailed and considered significant if P< 0.05. Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was performed to allocate the best cutoff point that maximizes the sum of sensitivity and specificity for the tested miRNA-373, VEGF, and cyclin D1 and to detect their cutoff points and predictive values that discriminate between the cancer and non-cancer groups [32]. The Mann-Whitney U and Kruskal-Wallis tests were carried out for non-parametric analyses, and the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and chi-square (χ2) tests were done as applicable. Correlations between investigated molecular markers were done using Spearman rank correlation.
Results
Demographic and clinico-pathologic data of investigated groups
As noticed in Table 1, among the entire groups, there was no significant difference reported between their ages and menopause status (P=0.923 and P= 0.059 respectively). According to the clinico-pathological criteria, patients with benign breast lesions were with follicular hyperplasia (n=36), fibrocystic changes (n=22), and intra-ductal papillomatsis (n=18), while those with newly diagnosed breast cancer were divided pathologically into duct carcinoma in situ (DCI) (n= 89, 45.4%) and invasive duct carcinoma (IDC) (107, 54.6%) and staged into stage 0–I (n= 57, 29.1%), stage (II) (n=53, 27%), stage (III) (n=70, 35.7%), and stage IV (n=16, 8.2%) and graded into grade I (n=64, 32.6%), grade II (n=58, 29.6%), and grade III (n=74, 37.8%). Lymph node (LN) involvements were detected in 95 of cases (48.5%), regarding hormonal status: positive estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PgR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER-2/neu) were positive in 67 (34.2%), 135 (68.9%), and 123 (62.8%), respectively.
Table 1.
Demographic and clinico-pathologic data of the investigated groups
| Parameter | Breast cancer | Benign patients | Healthy controls | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 196 | 76 | 49 | – |
| Age (years, mean±SD) | 52.4 ± 9.1 | 52.0 ± 9.3 | 52.0 ± 9.3 | 0.923a |
| Menopause status (no. (%)) | ||||
| Pre-menopausal | 114 (58.2%) | 39 (51.3%) | 28 (57%) | 0.059 |
| Post-menopausal | 82 (41.8%) | 37 (48.7%) | 21 (42.9%) | |
| Tumor invasion | ||||
| DCI | 89 (45.4%) | |||
| IDC | 107 (54.6%) | |||
| Tumor depth (stage) | ||||
| Stage I | 57 (29.1%) | |||
| Stage II | 53 (27%) | |||
| Stage III | 70 (35.7) | |||
| Stage IV | 16 (8.2%) | |||
| Tumor histological grade | ||||
| Grade I | 64 (32.6%) | |||
| Grade II | 58 (29.6%) | |||
| Grade III | 74 (37.8%) | |||
| Lymph node invasion | ||||
| Negative | 101 (51.5%) | |||
| Positive | 95 (48.5%) | |||
| ER | ||||
| Negative | 67 (34.2%) | |||
| Positive | 129 (65.8%) | |||
| PgR | ||||
| Negative | 61 (31.1%) | |||
| Positive | 135 (68.9%) | |||
| HER-2/neu status | ||||
| Negative | 73 (37.2%) | |||
| Positive | 123 (62.8%) | |||
P > 0.05 is considered non-significant; P < 0.05 is considered significant
DCI duct carcinoma in situ, IDC invasive duct carcinoma, ER estrogen receptor, PgR progesterone receptor, Her2/neu human epidermal growth factor receptor-2
aData were represented as mean ±SD
Expression of miRNA-373, VEGF, and cyclin D1 among the studied groups
As reported in Table 2, the mean rank level for miRNA-373 and investigated genes, VEGF and cyclin D1, reported a significant increase among primary breast cancer patients followed by benign cases while their expression were the lowest in healthy individual cases (P< 0.0001). Similarly, by plotting the ROC curve for discrimination between cancer and non-cancer groups (benign and healthy) (Fig. 1), a significant difference was reported (P< 0.0001) between the three groups as the frequency of the positivity rate (> cutoff point) was superior for breast cancer cases at 91.3%, 92.9%, and 91.8% for miRNA-373, VEGF, and cyclin D1, respectively.
Table 2.
Frequency distributions of investigated markers among different studied groups
| Groups | Markers | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEGF (fold change) | Cyclin D1 (fold change)a | miR-373 (fold change)a | |||||||
| Mean ranka | ≤ 38b | > 38 | Mean ranka | ≤ 38 | > 38 | Mean ranka | ≤ 360 | > 360 | |
| Healthy individuals | 32.86 | 49 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 30.92 | 49 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 27.04 | 49 (100%) | 0 (0%) |
| Benign lesions | 88.78 | 73 (96.1%) | 3 (3.9%) | 91.59 | 72 (94.7%) | 4 (5.3%) | 92.57 | 75 (98.7%) | 1 (1.3%) |
| Primary breast cancer | 221.05 | 14 (7.1%) | 182 (92.9%) | 220.43 | 16 (8.2%) | 180 (91.8%) | 221.03 | 17 (8.7%) | 179 (91.3%) |
aAnalysis using non-parametric mean rank test by Kruskal-Wallis test (as to calculate the average of the ranks for the marker among the enrolled groups)
bChi-square test with statistical significance at P< 0.0001
Fig. 1.
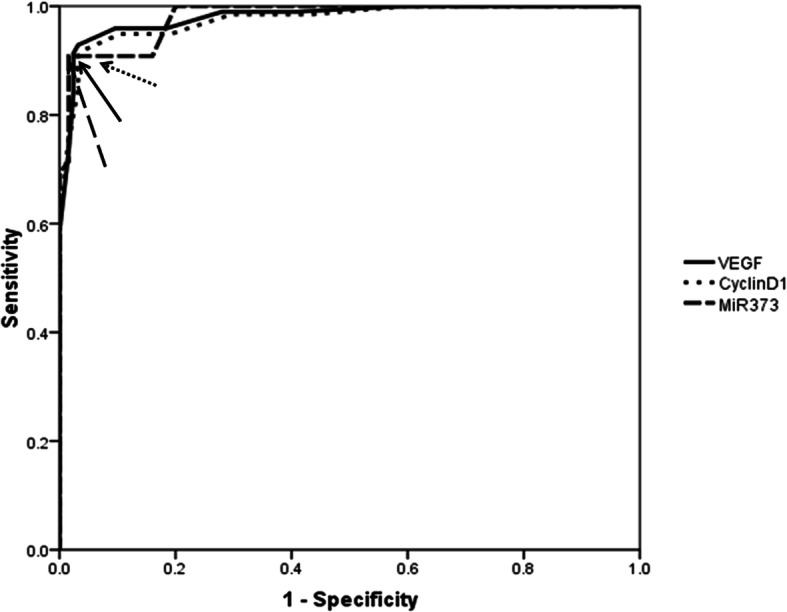
Receiver operating characteristic curve for investigated markers. Arrows donate to the cut value for investigated markers: for VEGF, the cutoff was 38 ng/ml with sensitivity at 92.35% and specificity at 96.8% at standard error 0.0077 and CI% 0.955–0.991, area under the curve 0.978; for cyclin D1, the cutoff was 38 ng/ml with sensitivity at 91.8% and specificity at 96% at standard error 0.008 and CI% 0.952–0.989, area under the curve 0.975; and for miR-373, the cutoff was 360 ng/ml with sensitivity at 90.8% and specificity at 98.4% at standard error 0.007 and CI% 0.958–0.992, area under the curve 0.98
Prognostic presentation of investigated markers among the breast cancer group
The mean rank levels for miRNA-373, VEGF, and cyclin D1 were investigated regarding clinico-pathological factors (age, menopausal status, pathological types, clinical stage, histological grading, and hormonal receptor status) among the primary breast cancer group. No significant difference (P>0.05) was reported between investigated markers and age or menopausal status.
miRNA-373 reported significant difference as shown in Fig. 2a with pathological types as their the mean rank levels were 111.48 in IDC as compared to 82.89 for DCI (P<0.001), also with clinical stages (Fig. 2b) 83.02, 107, 68, 96.42, and 128.97 with stages I, II, III, and IV, respectively (P=0.012). Regarding histological grading, a significant level (P=0.006) is reported at Fig. 2c as miRNA-373 expression level was elevated in advanced grade as compared to low ones. A significant difference was reported with lymph node status as lymph node involvement reported high mean rank miRNA-373 (117.7) as compared to negative LN involvement (80.4) (P<0.0010) as plotted in Fig. 2d. The relation between miRNA-373 and hormonal status is shown in Table 3.
Fig. 2.
Relation between miR-373 and clinico-pathological features. a Pathological types (DCI vs IDC) at X2=3.5 (P<0.001). b Clinical stages (stage I to IV) at X2=10 (P=0.012). c Histological grading (grade I to III) at X2=10 (P=0.006). d Lymph node involvement (negative involvement vs positive involvement) (X2=4.43, P<0.001). X2 resembles the chi-square test between investigated variables
Table 3.
Mean rank level of VEGF, cyclin D1, and miR-373 among the primary breast cancer group (n=196)
| Characteristics | VEGF | Cyclin D1 | miR-373 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ER status | |||
| Negative (n=20) | 84.8 | 90 | 82 |
| Positive (n=76) | 113 | 107 | 115 |
| Z= 3.5, P<0.001 | Z= 2.16, P= 0.031 | Z= 4, P<0.001 | |
| PgR status | |||
| Negative (n=35) | 86 | 97 | 91 |
| Positive (n=61) | 104 | 101 | 114 |
| Z= 3.4, P= 0.037 | NS | Z=2.6, P=0.008 | |
| HER-2/neu status | |||
| Negative (n=37) | 95.8 | 99.4 | 91 |
| Positive (n=51) | 100.08 | 98 | 110 |
| NS | NS | Z=2.28, P=0.022 | |
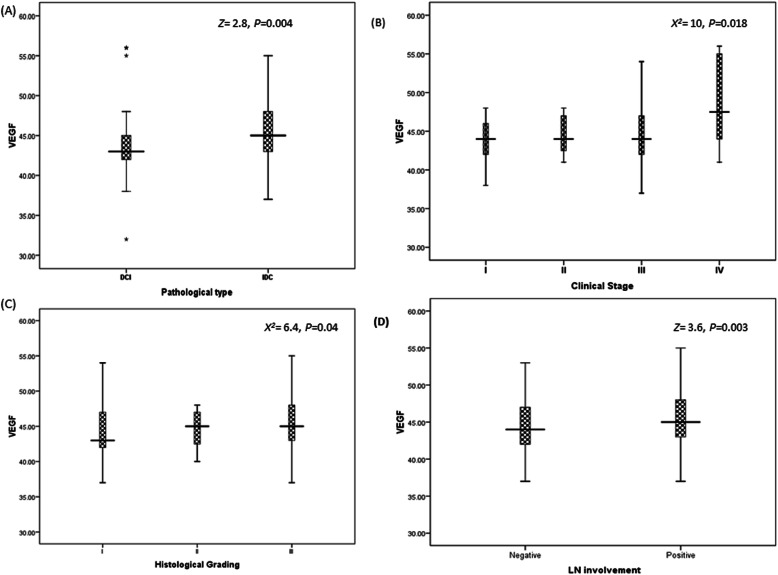
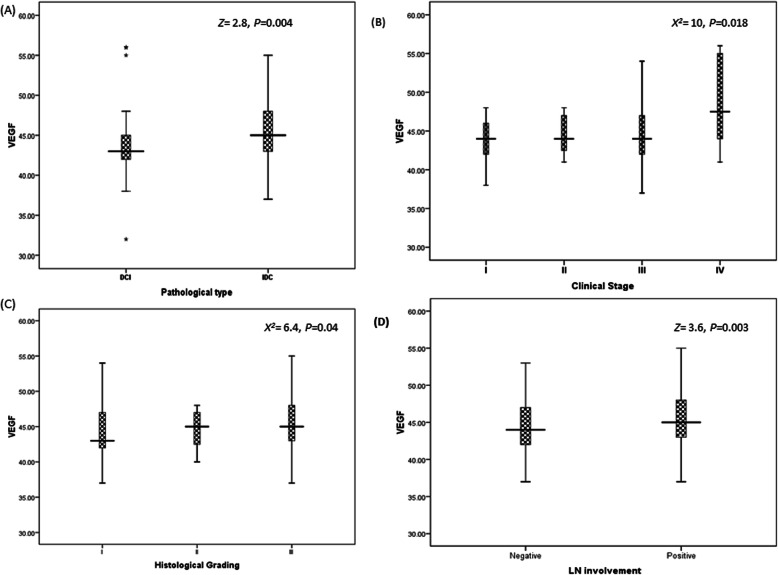
For VEGF, a significant level was reported between VEGF gene expression and pathological type as its level was significantly increased in IDC as 111.12 as compared to DCI which equals 86 (P=0.004) (Fig. 3a); also, a significant difference was reported with clinical stages (Fig. 3b); the mean rank levels reported 103.8, 101.37, 86.6, and 134.3 with stages I, II, III, and IV, respectively (P=0.018), similarly with grading as presented in Fig. 3c with mean ranks as 85.5, 97.9, and 110 for grades I, II, and III, respectively (P=0.04). LN status reported a significant difference with VEGF expression level as the mean rank for negative LN was 86.9 vs positive LN was 110.8 (P=0.003) (Fig. 3d). The impact of VEGF expression with hormonal receptor status is represented in Table 3.
Fig. 3.
Relation between VEGF and clinico-pathological features. a Pathological types (DCI vs IDC) at Z=2.8 (P=0.004). b Clinical stages (stage I to IV) at X2=10 (P=0.018). c Histological grading (grade I to III) at X2=6.4 (P=0.04). d Lymph node involvement (negative involvement vs positive involvement) (Z=3.6, P=0.003). Statistical analysis was done using the non-parametric test; as for two variables, the Mann-Whitney U test (Z-value) was used; and for more than two variables, the Kruskal-Wallis H test (X2 test) was used
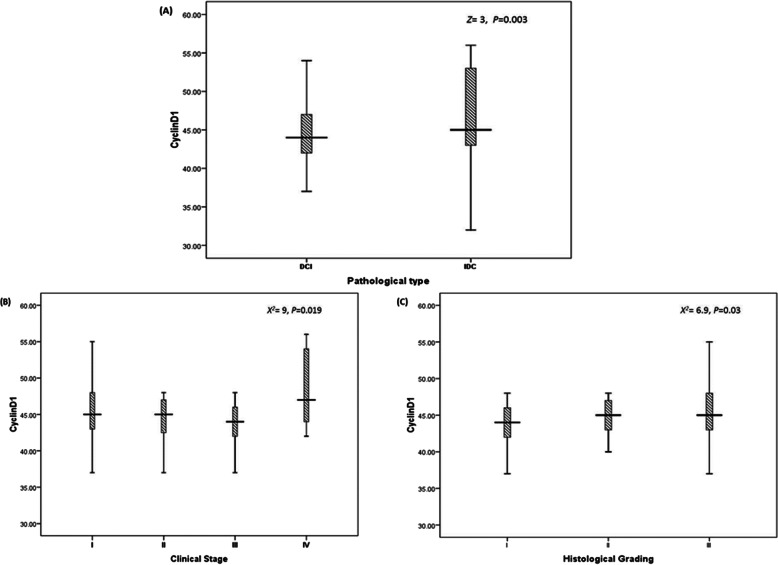
Regarding cyclin D1, a significant difference was reported with pathological classification as its expression elevated in IDC to be 111.67 as compared to 87.47 for DCI (P=0.003) (Fig. 4a). Also, the mean rank level reported significant difference with clinical stages as well; the mean rank levels reported in Fig. 4b 103.8, 96.79, 86.6, and 132 with stages I, II, III, and IV, respectively (P=0.019), also significant level with histological grading as 85.6, 97, and 110,8 for grades I, II, and III (P=0.03) as shown in Fig. 4c. The expression of cyclin D1 with hormonal status is represented in Table 3.
Fig. 4.
Relation between cyclin D1 and clinico-pathological features. a Pathological types (DCI vs IDC) at Z=3 (P=0.003). b Clinical stages (stage I to IV) at X2=9 (P=0.019). c Histological grading (grade I to III) at X2=6.9 (P=0.03). Statistical analysis was done using the non-parametric test; as for two variables, the Mann-Whitney U test (Z-value) was used; and for more than two variables, the Kruskal-Wallis H test (X2 test) was used
Correlation between miRNA and investigated genes
The correlation between miRNA-373 and both genes were significant (R = 0.352, P< 0.001) with VEGF and (R =0.365, P< 0.001) with cyclin D1. Also, the two genes were significantly correlated with each other (R =0.344, P< 0.001).
Discussion
Recently, evidence proposes that miRNAs have significant roles in various cellular events, and their expression patterns might be precious markers in the diagnosis of several cancer types and patient outcomes [33, 34]. To the best of our knowledge, the present study that was performed on the Egyptian cohort is the first which assesses the expression level of circulating miRNA-373 and its target genes including VEGF and cyclin D1 in blood specimens of BC patients.
There are several literatures demonstrating the oncogenic role of miRNA-373 through targeting various genes in several types of human cancer [35–40]. Nevertheless, to date, functions of miRNA-373 in BC remain debated [20], which motivated us to examine the role of miRNA-373 in BC; according to our results, high expression levels of circulating miRNA-373 were reported in primary breast cancer patients followed by benign cases compared to the lower expression levels in healthy volunteers. These results were consistent with Eichelser et al. [41]. Based on these findings, it seems that miRNA-373 and its target genes were valuable molecular biomarkers in the early prediction and diagnosis of BC, and in the discrimination between cancer and non-cancer cases.
A significant association was detected between miRNA-373 expression level and unfavorable prognostic factors for BC which agree with the previous report of Chen et al. [42], and this may be due to its role to promote BC invasion and metastasis by inhibiting the protein expression of the cell surface marker cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44) [21]. Moreover, it was able to trigger the Wnt/β-catenin-signaling pathway, which is implicated in both stem cell maintenance and tumorigenesis [43].
Angiogenesis plays a key role in the development of tumor growth and metastasis, VEGF is one of these angiogenic markers, and it has been overexpressed in breast cancer as compared to the other investigated groups which agreed with previous reports [44–46]. The association of the expression level of the VEGF gene with the clinico-pathological characteristics of BC was examined, and VEGF expression level was associated with IDC, high staging, high grading, lymph node metastasis, and finally hormonal status except HER2-neu status, which directs the importance of VEGF as both diagnostic and prognostic marker. Using of anti-angiogenic drugs as anti-VEGF drugs (Avastin (bevacizumab) or ranibizumab (Lucentis)) has effectually proved to prevent tumor growth specifically in combination with chemotherapy or immunotherapy [47]. As previously reported, the combination of bevacizumab with conventional chemotherapy can increase both survival and response to treatment in patients with different types of cancer [48–50].
Cyclin D1 expression was significantly increased in breast cancer patients as compared to both benign and control individuals; these findings were in line with Elsheikh and his colleagues [44] as they noted that a strong association between CCND1 amplification and its protein expression (cyclin D1) in breast cancer. Also, Ravikumar and Ananthamurthy [51] showed that high cyclin D1 expression was identified 67.5% in ductal carcinoma. Moreover, Hartel et al. [52] reported that cyclin D1 expression may serve as a marker for more biologically aggressive triple-negative breast cancer. Additionally, Ortiz et al. [53] showed that high cyclin D1 expression was identified in 67.5% in ductal carcinoma and 52% of invasive breast cancers. In respect to the association of cyclin D1 expression level with the clinico-pathological features of BC, our findings showed that the overexpression of cyclin D1 was associated with IDC, high staging, high grading, lymph node metastasis, and finally hormonal status except HER2-neu status. Cyclin D1 expression was correlated with ER expression [54] in agreement with our findings. These results indicate the vital role of cyclin D1 in estrogen-induced breast cancer, as estrogen action is induced through transcriptional activation of cyclin D1 and cellular-Myc (c-Myc) [55–57].
The relation between miRNA-373 and the studied genes was investigated and reported significant correlation which agreed with the previous study reported a relation between the overexpression of miRNA-373 and VEGF gene in cancerous tissues that emphasized the fact that miRNA-373 acts as an essential factor in tumorigenesis and metastasis [36]. In contrast to our results, Tavazoie et al. [22] reported that miRNA-373 is a metastasis-promoting factor through inhibiting the expression of cyclin D1.
Conclusion
miRNA-373 expression is considered an oncomir that is related to VEGF and cyclin D1 expression, and all were related to tumorigenesis. Hence, their detection in circulating blood may aid in better early diagnosis of breast cancer, and prognosis of such disease. Thus, it is recommended to investigate these findings on a large number of cases as their uses in clinical practice may aid in the early detection of breast cancer and help in targeted therapy.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- BC
Breast cancer
- VEGF
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- QPCR
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- G0
Gap 0
- CDK
Cyclin-dependent kinase
- pRb
Retinoblastoma protein
- ESC
Human embryonic stem cell
- RAS
Rat sarcoma
- MTIs
miRNA-target interactions
- ILC
Invasive lobular carcinoma
- TNBC
Tiple-negative breast cancer
- EDTA
Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid
- Ct
Cycle threshold
- SPSS
Statistical Package for Social Sciences
- ROC
Receiver operating characteristic curve
- ANOVA
One-way analysis of variance
- SE
Standard error
- DCI
Duct carcinoma in situ
- IDC
Invasive duct carcinoma
- LN
Lymph node
- ER
Estrogen receptor
- PgR
Progesterone receptor
- HER-2/neu
Human epidermal growth factor receptor
- CD44
Cluster of differentiation 44
- c-Myc
Cellular-Myc
- G1
Gap 1
- S
Synthesis phase
Authors’ contributions
NMB and MS: study conceptualization and design. RN and HB: provision of blood sampling and clinical follow-up. NMB: methodology. NMB: acquisition of data and writing of the manuscript. NMB and MSM: analysis and interpretation of the data. NMB: drafting of the manuscript. NMB and MS: critical revision. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported equally through a grant from Science and Technology Development Fund (STDF) through the Basic and Applied Research Support Grant Project (BARG) [No.15089], Egypt. The instruments listed in the current study were purchased through a grant from Science and Technology Development Fund (STDF) through the Capacity Building Grant Project (CBG) [No. 4940].
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This research paper was approved by the ethics committee (Medical Research Ethics Committee of National research center, Cairo, Egypt) with approval number 15029. The participants provided written consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Fang R, Zhu Y, Hu L, Khadka VS, Ai J, Zou H. Plasma microRNA pair panels as novel biomarkers for detection of early stage breast cancer. Front Physiol. 2019;9:1879. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Katz B, Tropé CG, Reich R, Davidson B. MicroRNAs in ovarian cancer. Hum Pathol. 2015;46(9):1245–1256. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2015.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81683-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fouad YA, Aanei C. Revisiting the hallmarks of cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2017;7(5):1016–1036. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Baig B, Halim SA, Farrukh A, Greish Y, Amin A. Current status of nanomaterial-based treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;116:108852. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lugano R, Ramachandran M, Dimberg A. Tumor angiogenesis: causes, consequences, challenges and opportunities. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77(9):1745–1770. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03351-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nahta R, Al-Mulla F, Al-Temaimi R, Amedei A, Andrade-Vieira R, Bay SN, et al. Mechanisms of environmental chemicals that enable the cancer hallmark of evasion of growth suppression. Carcinogenesis. 2015;36(Suppl. 1):S2–S18. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Amin A, Bajbouj K, Koch A, Gandesiri M, Schneider-Stock R. Defective autophagosome formation in p53-null colorectal cancer reinforces crocin-induced apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(1):1544–1561. doi: 10.3390/ijms16011544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Graham TA, Sottoriva A. Measuring cancer evolution from the genome. J Pathol. 2017;241(2):183–191. doi: 10.1002/path.4821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jin YJ, Lee JH, Kim YM, Oh GT, Lee H. Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 stimulates proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by up-regulating cyclins D1 and E through the PI3K/Akt-, ERK-, and JNK-dependent AP-1 and E2F activation signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 2012;24(8):1485–1495. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang G, Gormley M, Qiao J, Zhao Q, Wang M, Di Sante G, et al. Share cyclin D1-mediated microRNA expression signature predicts breast cancer outcome. Theranostics. 2018;8(8):2251–2263. doi: 10.7150/thno.23877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ramjiawan RR, Griffioen AW, Duda DG. Anti-angiogenesis for cancer revisited: is there a role for combinations with immunotherapy? Angiogenesis. 2017;20(2):185–204. doi: 10.1007/s10456-017-9552-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Al-Dabbagh B, Elhaty IA, Murali C, Al Madhoon A, Amin A. Salvadora persica (Miswak): antioxidant and promising antiangiogenic insights. Am J Plant Sci. 2018;9(6):1228–1244. doi: 10.4236/ajps.2018.96091. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Petrovic N. Targeting angiogenesis in cancer treatments: where do we stand? J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2016;19(2):226–238. doi: 10.18433/J30033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yehya AHS, Asif M, Petersen SH, Subramaniam AV, Kono K, Majid AMSA, Oon C. Angiogenesis: managing the culprits behind tumorigenesis and metastasis. Medicina (Kaunas) 2018;54(1):8. doi: 10.3390/medicina54010008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Di Leva G, Briskin D, Croce CM. MicroRNA in cancer: new hopes for antineoplastic chemotherapy. Ups J Med Sci. 2012;117(2):202–216. doi: 10.3109/03009734.2012.660551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sun M, Liu XH, Li JH, Yang JS, Zhang EB, Yin DD, Liu ZL, Zhou J, Ding Y, Li SQ, Wang ZX, Cao XF, de W. MiR-196a is upregulated in gastric cancer and promotes cell proliferation by downregulating p27 (kip1) Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(4):842–852. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, Gillis AJ, Stoop H, Nagel R, et al. A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Cell. 2006;124(6):1169–1181. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jiang S, Zhang HW, Lu MH, He XH, Li Y, Gu H, Liu MF, Wang ED. MicroRNA-155 functions as an OncomiR in breast cancer by targeting the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 gene. Cancer Res. 2010;70(8):3119–3127. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wei F, Cao C, Xu X, Wang J. Diverse functions of miR-373 in cancer. J Transl Med. 2015;13(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0523-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Huang Q, Gumireddy K, Schrier M, le Sage C, Nagel R, Nair S, Egan DA, Li A, Huang G, Klein-Szanto AJ, Gimotty PA, Katsaros D, Coukos G, Zhang L, Puré E, Agami R. The microRNAs miR-373 and miR-520c promote tumour invasion and metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(2):202–210. doi: 10.1038/ncb1681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tavazoie SF, Alarcón C, Oskarsson T, Padua D, Wang Q, Bos PD, Gerald WL, Massagué J. Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2008;451(7175):147–152. doi: 10.1038/nature06487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rakha EA, Green AR, Powe DG, Roylance R, Ellis IO. Chromosome 16 tumor-suppressor genes in breast cancer. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2006;45(6):527–535. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Velasco-Velázquez MA, Li Z, Casimiro M, Loro E, Homsi N, Pestell RG. Examining the role of cyclin D1 in breast cancer. Future Oncol. 2011;7(6):753–765. doi: 10.2217/fon.11.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.O’Leary B, Finn RS, Turner NC. Treating cancer with selective CDK4/6 inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016;13(7):417–430. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tchakarska G, Sola B. The double dealing of cyclin D1. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(2):163–178. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1706903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.He T, Qi F, Jia L, Wang S, Song N, Guo L, Fu Y, Luo Y. MicroRNA-542-3p inhibits tumour angiogenesis by targeting angiopoietin-2. J Pathol. 2014;232(5):499–508. doi: 10.1002/path.4324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Luengo-Gil G, Gonzalez-Billalabeitia E, Perez-Henarejos SA, Navarro Manzano E, Chaves-Benito A, Garcia-Martinez E, Garcia-Garre E, Vicente V, Ayala de la Peña F. Angiogenic role of miR-20a in breast cancer. PLoS One. 2018;3(4):e0194638. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Perrot-Applanat M, Di Benedetto M. Autocrine functions of VEGF in breast tumor cells: adhesion, survival, migration and invasion. Cell Adhes Migr. 2012;6(6):547–553. doi: 10.4161/cam.23332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Robbins P, Pinder S, de Klerk N, Dawkins H, Harvey J, Sterrett G. Histological grading of breast carcinomas: a study of interobserver agreement. Hum Pathol. 1995;26(8):873–879. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zweig MH, Campbell G. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) plots: a fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin Chem. 1993;39(4):561–577. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/39.4.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tutar Y. miRNA and cancer; computational and experimental approaches. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014;15(5):429. doi: 10.2174/138920101505140828161335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dahiya N, Morin PJ. MicroRNAs in ovarian carcinomas. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010;17(1):F77–F89. doi: 10.1677/ERC-09-0203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhang X, Li X, Tan Z, Liu X, Yang C, Ding X, et al. MicroRNA-373 is upregulated and targets TNFAIP1 in human gastric cancer, contributing to tumorigenesis. Oncol Lett. 2013;6(5):1427–1434. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Liu W, Li M, Chen X, Zhang D, Wei L, Zhang Z, Wang S, Meng L, Zhu S, Li B. MicroRNA-373 promotes migration and invasion in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting TIMP3 expression. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;6(1):1–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tu HF, Chang KW, Cheng HW, Liu CJ. Upregulation of miR-372 and -373 associates with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis of oral carcinomas. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(11):E365–E370. doi: 10.1002/lary.25464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Li Y, Zhang D, Wang J. MicroRNA 373 promotes tumorigenesis of renal cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(5):7048–7055. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bai X, Yang M, Xu Y. MicroRNA-373 promotes cell migration via targeting salt-inducible kinase 1 expression in melanoma. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(6):4759–4764. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Saeidi N, et al. Evaluation of circulating miRNA146a, miRNA155 and miRNA373 as potential biomarkers in ovarian cancer detection. J Mol Genet Med. 2018;12:3. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Eichelser C, Flesch-Janys D, Chang-Claude J, Pantel K, Schwarzenbach H. Deregulated serum concentrations of circulating cell-free microRNAs miR 17, miR-34a, miR-155, and miR 373 in human breast cancer development and progression. Clin Chem. 2013;59(10):1489–1496. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2013.205161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chen W, Cai F, Zhang B, Barekati Z, Zhong XY. The level of circulating miRNA-10b and miRNA-373 in detecting lymph node metastasis of breast cancer: potential biomarkers. Tumour Biol. 2013;34(1):455–462. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0570-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hafez MM, Hassan ZK, Zekri AR, Gaber AA, Al Rejaie SS, Sayed-Ahmed MM, et al. MicroRNAs and metastasis-related gene expression in Egyptian breast cancer patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(2):591–598. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.2.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Elsheikh S, Green AR, Aleskandarany MA, Grainge M, Paish CE, Lambros MB, et al. CCND1 amplification and cyclinD1 expression in breast cancer and their relation with proteomic subgroups and patient outcome. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;109(2):325–335. doi: 10.1007/s10549-007-9659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bender RJ, Mac GF. Expression of VEGF and semaphoring genes define subgroups of triple negative breast cancer. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e61788. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Li X, Gao Y, Li J, Zhang K, Han J, Li W, Hao Q, Zhang W, Wang S, Zeng C, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Li M, Zhang C. FOXP3 inhibits angiogenesis by downregulating VEGF in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(7):744. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0790-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Teleanu RI, Chircov C, Grumezescu AM, Teleanu DM. Tumor angiogenesis and anti-angiogenic strategies for cancer treatment. J Clin Med. 2020;9(1):84. doi: 10.3390/jcm9010084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gray R, Bhattacharya S, Bowden C, Miller K, Comis RL. Independent review of e2100: a phase iii trial of bevacizumab plus paclitaxel versus paclitaxel in women with metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(30):4966–4972. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.6630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Miles DW, Chan A, Dirix LY, Cortés J, Pivot X, Tomczak P, Delozier T, Sohn JH, Provencher L, Puglisi F, Harbeck N, Steger GG, Schneeweiss A, Wardley AM, Chlistalla A, Romieu G. Phase iii study of bevacizumab plus docetaxel compared with placebo plus docetaxel for the first-line treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(20):3239–3247. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.6457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Robert NJ, Dieras V, Glaspy J, Brufsky AM, Bondarenko I, Lipatov ON, et al. Ribbon-1: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase iii trial of chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for first-line treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative, locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(10):1252–1260. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.28.0982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ravikumar G, Ananthamurthy A. Cyclin D1 expression in ductal carcinoma of the breast and its correlation with other prognostic parameters. J Cancer Res Ther. 2014;10(3):671–675. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.138135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hartel PH et al (2016) Cyclin D1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer with new treatment implications. Clin Oncol 1:1044
- 53.Ortiz AB, Garcia D, Vicente Y, Palka M, Bellas C, Martin P. Prognostic significance of cyclin D1 protein expression and gene amplification in invasive breast carcinoma. PLoS One. 2017;12(11):e0188068. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Reis-Filho JS, Savage K, Lambros MB, James M, Steele D, Jones RL, et al. Cyclin D1 protein overexpression and CCND1 amplification in breast carcinomas: an immunohistochemical and chromogenic in situ hybridisation analysis. Mod Pathol. 2006;19(7):999–1009. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Prall OW, Rogan EM, Musgrove EA, Watts CK, Sutherland RL. L. c-Myc or cyclin D1 mimics estrogen effects on cyclin E-Cdk2 activation and cell cycle reentry. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18(8):4499–4508. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.8.4499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Roy PG, Pratt N, Purdie CA, Baker L, Ashfield A, Quinlan P, et al. High CCND1 amplification identifies a group of poor prognosis women with estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:355–360. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Peurala E, Koivunen P, Haapasaari KM, Bloigu R, Jukkola-Vuorinen A. The prognostic significance and value of cyclin D1, CDK4 and p16 in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(1):R5. doi: 10.1186/bcr3376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.