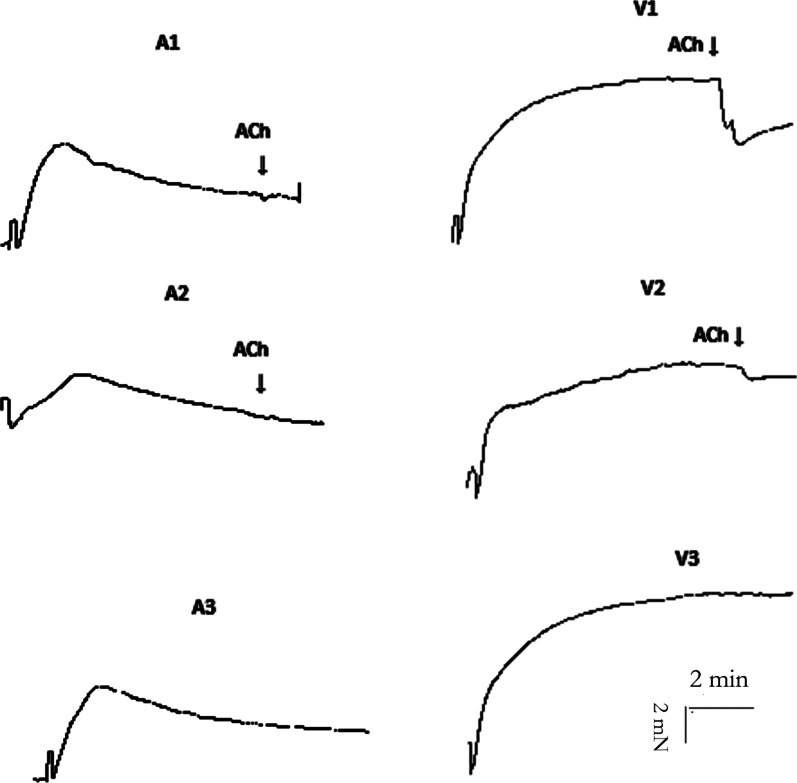
Fig. 5.
Responses of pulmonary arteries and veins to KCl and acetylcholine. Isometric tension recording of the effect of potassium chloride (KCl, 60 mM) on the pulmonary artery and vein segments from rats (endothelial integrity: N = 14; endothelium damage: N = 3; incubation with L-NAME: N = 5) (original trace). The number of rats is the number of repetitions of each group. A1–A3 represent the response to KCl stimulation of the pulmonary arteries with regard to endothelial integrity, endothelium damage and after incubation with L-NAME, respectively. V1–V3 represent the response to KCl stimulation of pulmonary veins with regard to endothelial integrity, endothelium damage and after incubation with L-NAME, respectively. After the contractions stabilized, the segments were exposed to a single high concentration of acetylcholine (ACh, 10− 3 M) (arrows)