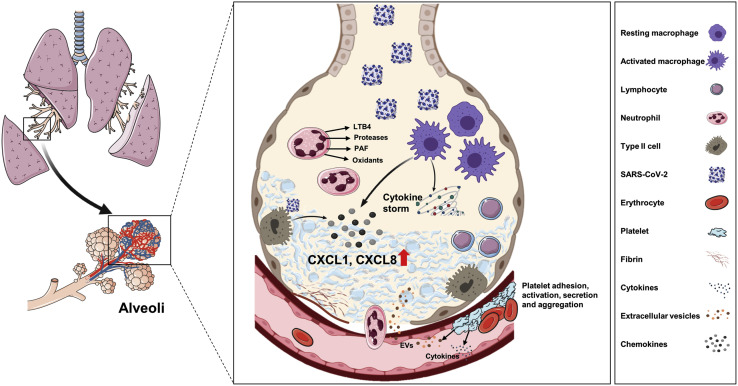
Fig 7.
Proposed lung pathophysiology associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. The SARS-CoV-2 virus infects type II pneumocytes and activates macrophages, causing the release of several cytokines and chemokines, including CXCL8 and CXCL1. The viral infection itself and various cytokines cause endothelial activation and dysfunction, resulting in vascular inflammation and permeability. Immune cells such as neutrophils and lymphocytes migrate into alveoli in response to the secreted chemoattractants and enhance lung inflammation. Damaged endothelial cell barrier causes platelet activation and aggregation as well as microthrombi formation. Together, inflammation, edema, and microthrombi cause ARDS.