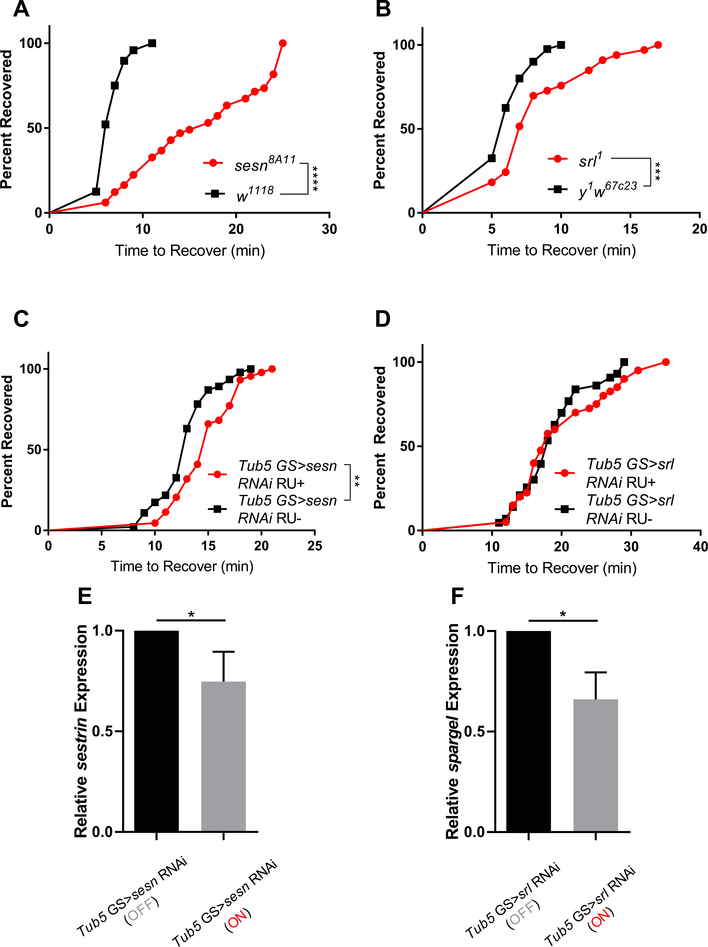
Fig. 1.
sestrin and spargel are required for normal chill coma recovery. sestrin (sesn8A11) and spargel (srl1) mutants were subjected to 2 h of cold exposure at 0 °C and monitored for recovery. (A) sestrin mutants took significantly longer to recover from chill coma (n ≥ 47 each group; p < 0.0001; log-rank test). (B) spargel mutants took significantly longer to recover from chill coma (n ≥ 33 each group; p < 0.0003; log-rank test). (C) Ubiquitous knockdown of sestrin under control of GS-Tub5-Gal4 driver significantly increased chill coma recovery time (n ≥ 44 each group; p = 0.001; log-rank test) (D) Ubiquitous knockdown of spargel did not significantly extend recovery time. (E,F) Relative sestrin and spargel transcript normalized to vehicle treated controls. Flies were 5–7 days old (n = 3 biological replicates each group; p = 0.04 and p = 0.01 for Tub5 GS > sesn RNAi groups and Tub5 GS > srl RNAi groups, respectively; unpaired t-test). ‘On’ indicates RU486 treated groups and ‘Off’ indicates vehicle treated groups.