Fig. 1.
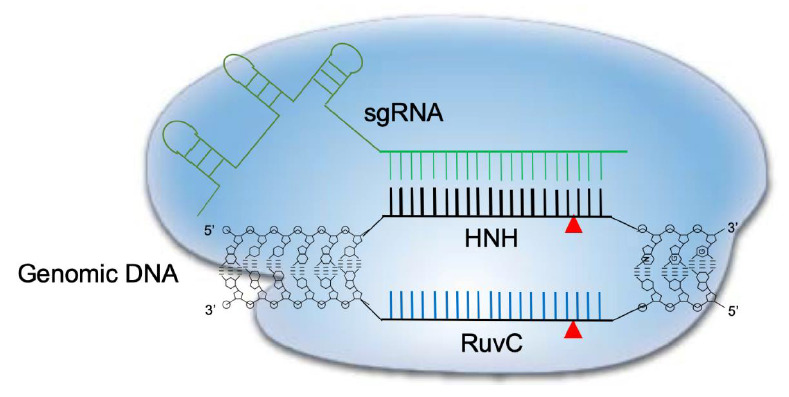
Schematic diagram of CRISPR-Cas9 cleavage of double-stranded DNA. The Cas9 dependent protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) genomic sequence is NGG. A 20-nucleotide long sequence is targeted by a complementary RNA (sgRNA) and structural RNAs responsible for Cas9 enzyme recruitment. Once the sgRNA binds the target sequence, Cas9’s HNH-like endonuclease cuts the 3’ position end of the PAM motif. At the same time, the nontargeting genomic strand is cleaved by the RuvC-like domain in Cas9, leading to a double-strand break. CRISPR-Cas9, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats and CRISPR-associated protein 9.
