Fig. 2.
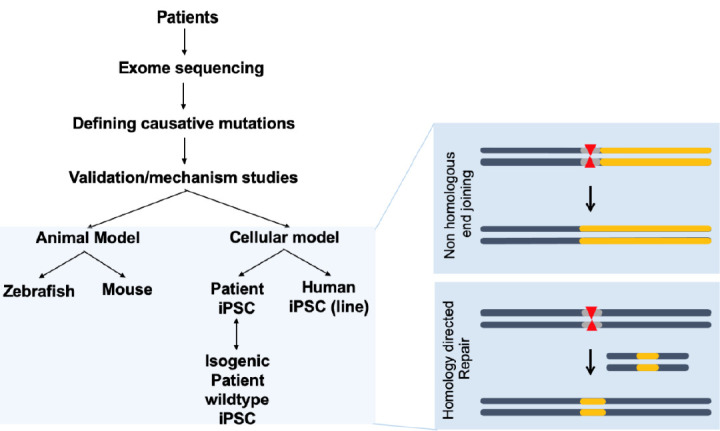
CRISPR-Cas9 applications for human congenital heart disease (CHD). Human samples such as white blood cells can be used for exome sequencing to detect novel genetic variations with single nucleotide resolution. Identification of novel mutations causing CHD can be validated in animal models such as mice or zebrafish, which are amenable to genetic manipulation. Application of CRISPR-Cas editing in both animal models and in vitro systems, such as induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) or differentiated cells derived from iPSCs, can validate the editing design. CRISPR-Cas9, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats and CRISPR-associated protein 9.
