Figure 1.
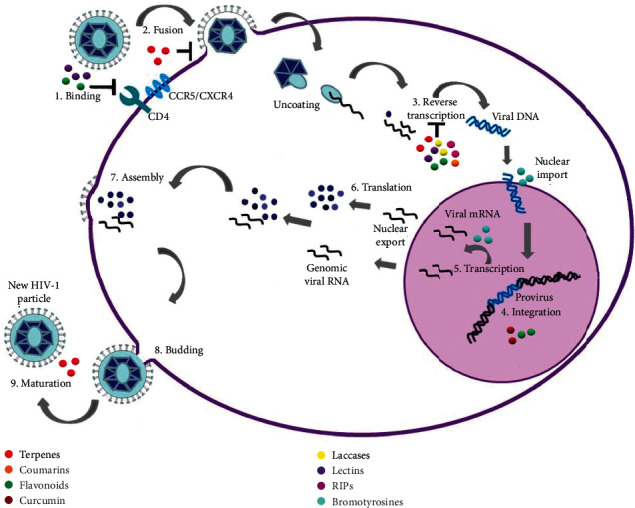
HIV-1 replication cycle exhibiting the sites of action of different natural products with anti-HIV-1 activity. Evidence suggests that flavonoids and lectins have an inhibitory effect on viral binding (1); terpenes inhibit virus fusion (2), whereas laccases, ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs), lectins, flavonoids, coumarins, and terpenes act on reverse transcriptase (3). Conversely, flavonoids and curcumin inhibit viral DNA integration (4), and bromotyrosines act on the transcription of the viral DNA (5). Finally, it has been reported that several terpenes act as inhibiting protease-mediated maturation of viral particles (9).
