FIGURE 2.
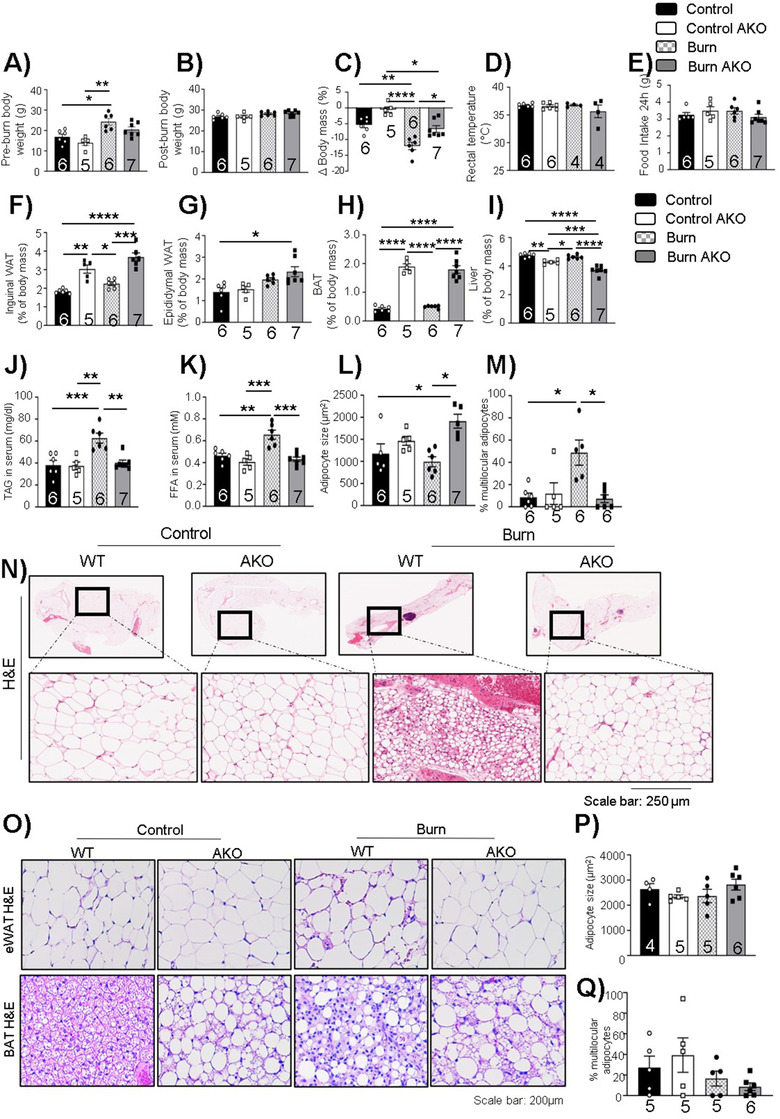
Adipose‐specific ATGL deletion impact on body weight and adipose tissue post‐burn injury: Twelve‐week‐old ATGL floxed and knockout mice were treated with 30%TBSA injury and monitored daily for 7 days. (A) Pre‐burn body weight. (B) Post‐burn body weight. (C) Change in body mass on day 7 in comparison to day 0. (D) Rectal temperature at day 7 of individual mice. (E) Food intake (24 h) at day 7 of individual mice. (F) Inguinal white adipose tissue (iWAT). (G) Epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT). (H) Brown adipose tissue (BAT), and (I) Liver normalized to the body weight of individual mice. (J) Triacylglycerol (TAG) content in serum samples. (K) Free fatty acid levels in serum samples. (L) Adipocyte size of adipocytes in iWAT. (M) Percentage of normalized multilocular adipocytes normalized to total number of adipocytes in sections of iWAT. (N) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining (zoom in and zoom out images of whole fat pad) in WAT samples. (O) Hematoxylin staining of epididymal and brown adipose tissue. (P) Adipocyte size of adipocytes in eWAT. (Q) Percentage of normalized multilocular adipocytes normalized to total number of adipocytes in sections of epididymal adipose tissue. The results displayed are the average and SEM analyzed in the specified number of mice samples. Statistical significance was assessed using two‐way ANOVA as appropriate
