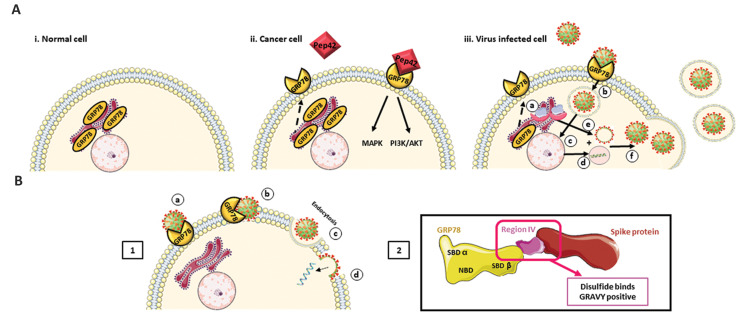
Fig.1.
GRP78 in different conditions. A. i. Normal cells. GRP78 is an important chaperone in endoplasmic reticulum. ii. Cancer cells. In cancerous cells, GRP78 is translocated to the cell membrane and comprises as a receptor. The main ligand for CS-GRP78 is Pep42 that activates certain pathways at the down-stream and initiate cancerous phenotypes. iii. Virus-infected Cells. GRP78 translocated to the cell surface. CS-GRP78 as a receptor at the cell surface facilitates viral entry into the cell and amplification and release of new viral generations from the host cell. B. 1. The proposed mechanism of virus entry through GRP78 receptor. 2. The required energy for virus entry provided by the ABD. CS-GRP78 can interconnect with S protein of SARS-CoV-2 by its SBDβ domain through the constituted disulfide and hydrophobic bonds. ABD; ATP binding domain, CS-GRP78; Cell surface glucose regulated protein 78, NBD; Nucleotide binding domain, SARS-CoV-2; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, and SBDβ; Substrate binding domain β.