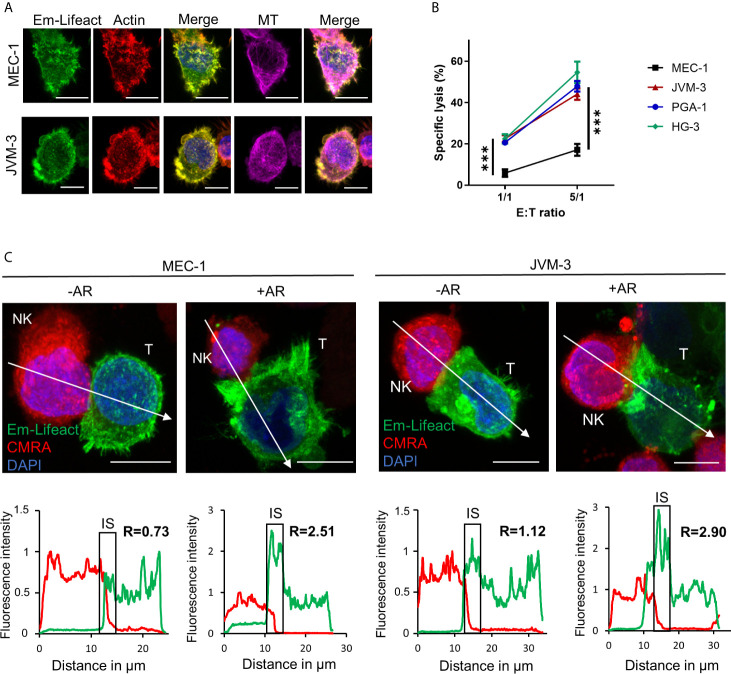
Figure 1.
CLL cells have the ability to respond to NK cell attack with an actin response associated to their resistance. (A) JVM-3 and MEC-1 cells were transduced to express the actin cytoskeleton marker Emerald-Lifeact (green). Stable cell lines were stained with Acti-stain 555 phalloidin (red) and anti-tubulin antibody (MT, violet). The yellow-green signal shows the co-localization of the two actin cytoskeleton probes. Bars: 10 µm. (B) Cytotoxicity assays with four CLL target cell lines and effector NK-92MI cells at 1:1 and 5:1 E:T ratios for 4 hrs. 2-way ANOVA was applied to determine statistical significance; *** denotes p < 0.0001. (C) Confocal microscopy pictures of MEC-1 (left) and JVM-3 (right) cells (T) in conjugation with NK-92MI cells (NK) with and without an actin response. The charts below show the relative fluorescent intensity of Emerald-Lifeact and CMRA along the trajectories (white arrow). The fluorescence was normalized to 1 at the opposite site of the synapse. The region of the immunological synapse is indicated with “IS”. Compared to the opposing end, target cells with an actin response have a more than 2-fold higher fluorescent signal at the IS. Bars: 10µm.