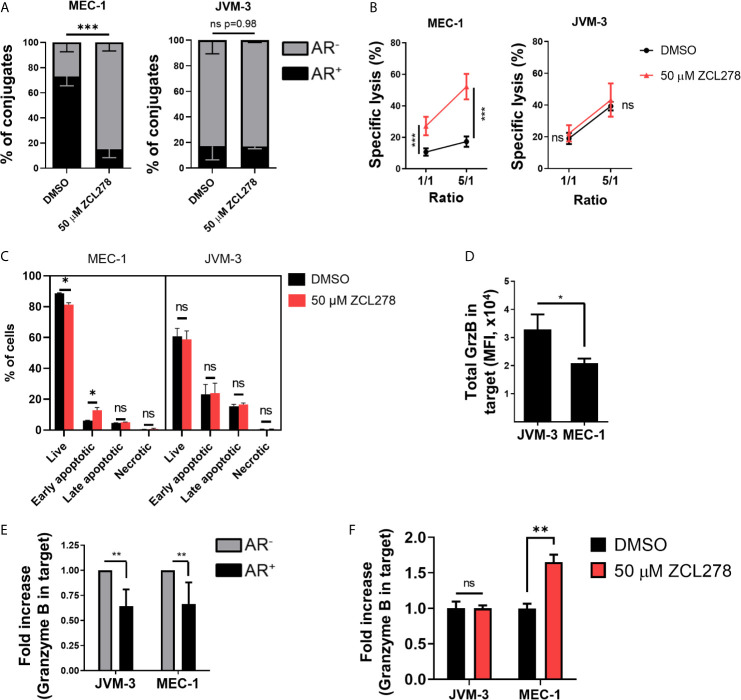
Figure 3.
Pharmacological inhibition of Cdc42 increases CLL cell susceptibility to NK cell attack by lowering actin response frequency. (A) Quantitative Imagestream analysis of CLL-NK cell conjugates. CLL cells were pre-treated with 50 µM ZCL278 and analyzed for their actin response frequency in conjugates with NK-92MI cells. *** denotes p < 0.0001 (B) NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity against DMSO- or ZCL278-treated CLL cells. Pre-treated JVM-3 and MEC-1 cells were co-cultured for 4 hrs with NK-92MI cells at E:T ratios of 1:1 and 5:1. Cell death was evaluated by To-Pro-3 staining and adjusted to NK cell-specific lysis. *** denotes p < 0.0001 (C) Flow cytometry analysis of DMSO- or ZCL278-pretreated CLL target cells after 45 minutes of co-culture with effector NK-92MI cells at a 1:1 E:T ratio. Apoptosis was evaluated by Annexin V and PI staining. * denotes p < 0.05, ** denotes p < 0.001, *** denotes p < 0.0001 (D) Imagestream analysis of total granzyme B load in target cells conjugated to NK-92MI cells after 45 minutes of co-culture. * denotes p < 0.05 (E) Target cells were categorized into AR+ (black) and AR- (grey) and granzyme B load in target cells evaluated. Data was normalized to AR- conjugates. ** denotes p < 0.001 (F) Imagestream analysis of intracellular granzyme B in target cells after ZCL278-induced Cdc42 inhibition. ** denotes p < 0.001. ns, non significant.