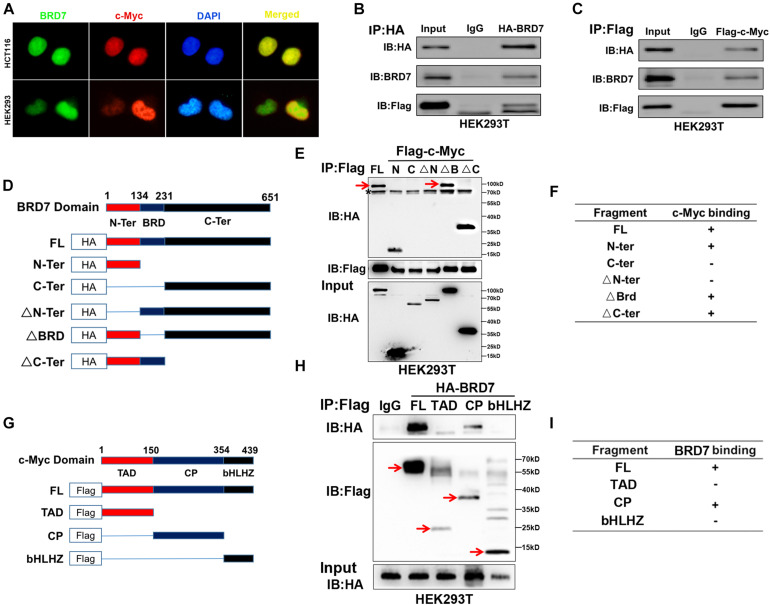
FIGURE 4.
BRD7 interacts with c-Myc in a manner dependent on the N-terminus of BRD7 and the CP-domain of c-Myc. (A) Immunofluorescence assays showed the localization of BRD7 and c-Myc in HCT116 and HEK293 cells. (B,C) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) confirmed the interaction between BRD7 and c-Myc in HEK293T cells. (D,G) The schematic diagram of different truncated mutants of BRD7 and c-Myc domains. (E,F,H,I) Co-IP assays revealed the structural basis of the interaction between BRD7 and c-Myc. The antibody used for IP detection in (E,H) is anti-Flag antibody, and the antibodies used for IB detection are anti-HA and anti-Flag antibodies, respectively. Of them, Flag was used to tag c-Myc and its mutants, while HA was used to tag BRD7 and its mutants. FL, full length; TAD, transcription activation domain; CP, central portion flanked by TAD and bHLHZ; bHLHZ, basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper; N-Ter/N, N-terminal; C-Ter/C, C-terminal; ΔN-Ter/ΔN, N-terminal deletion; ΔBRD, bromodomain deletion; ΔC-Ter/ΔC, C-terminal deletion. The arrow indicates the destination bands, and * indicates non-specific bands.