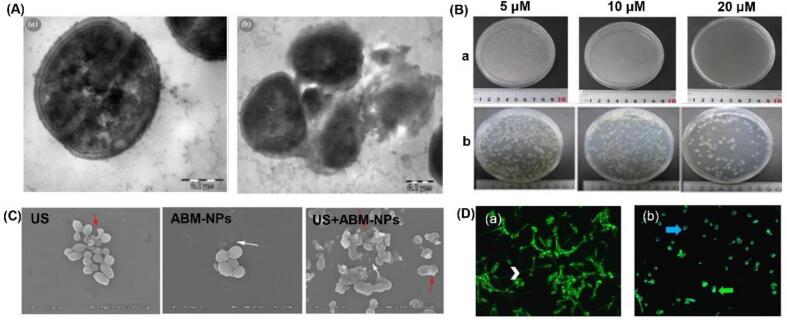
Fig. 3.
(A) Morphologies of control group (a) and S. aureus treated with ultrasound and antibiotics (b). Adapted from [58]; (B) Chlorin e6 with ultrasound treatment inhibited bacterial growth of S. aureus (a) and E. coli (b) in a dose-dependent manner. Adapted from [12]; (C) The morphological changes of C. albicans observed under SEM after distinct treatment methods. US, ultrasound alone. Adapted from [13]; (D) Light and fluorescence microscope images of the control group (a) and biofilms treated with a PDT + SDT PDZ 200 (b). The TB solution stained the nuclei of dead cells (blue arrow) and the Con-A bound to the polysaccharide cell wall with green fluorescence (green arrow). Adapted from [60]. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)