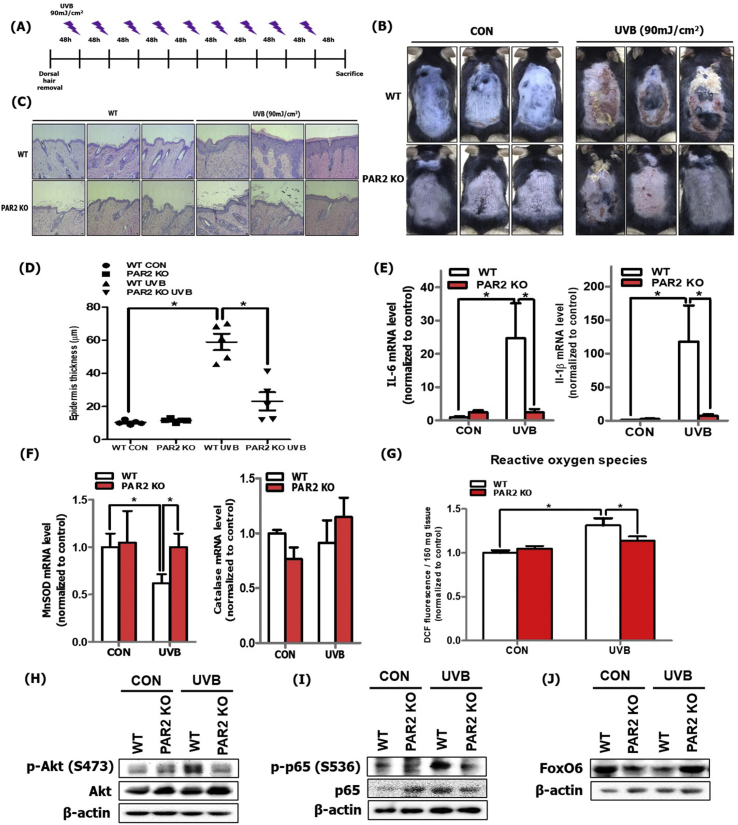
Fig. 4.
PAR2 KO mice showed reduced oxidative stress and inflammation during skin photoaging. (A) The experimental procedure for induction of UVB-irradiated skin photoaging using C57BL/6-strained WT and PAR2 KO mice (N = 5 per group). (B) Photographs of dorsal skin of control and UVB-irradiated mice of WT and PAR2 KO mice were taken for phenotype analysis. (B) H&E-stained histological image of a skin section of the control and UVB-irradiated WT and PAR2 KO mice was captured and (C) epidermal thickness was measured and (D) quantified using Motic Image Plus 2.0 software (N = 5 per group). (E) The mRNA levels of IL-6 and IL-1β and (F) MnSOD and catalase were quantified using qRT-PCR (N = 5 per group). (G) ROS production was determined by measuring DCF fluorescence level in the skin cytosol fraction (N = 5 per group). (H) The protein expression levels of phosphorylated Akt, total-Akt (I) phosphorylated p65, p65, and (J) total FoxO6 were detected using western blotting (N = 5 per group). β-actin was the loading control. All data are represented as the mean ± SEM, and significance was determined using an one-factor ANOVA; *P < 0.05.