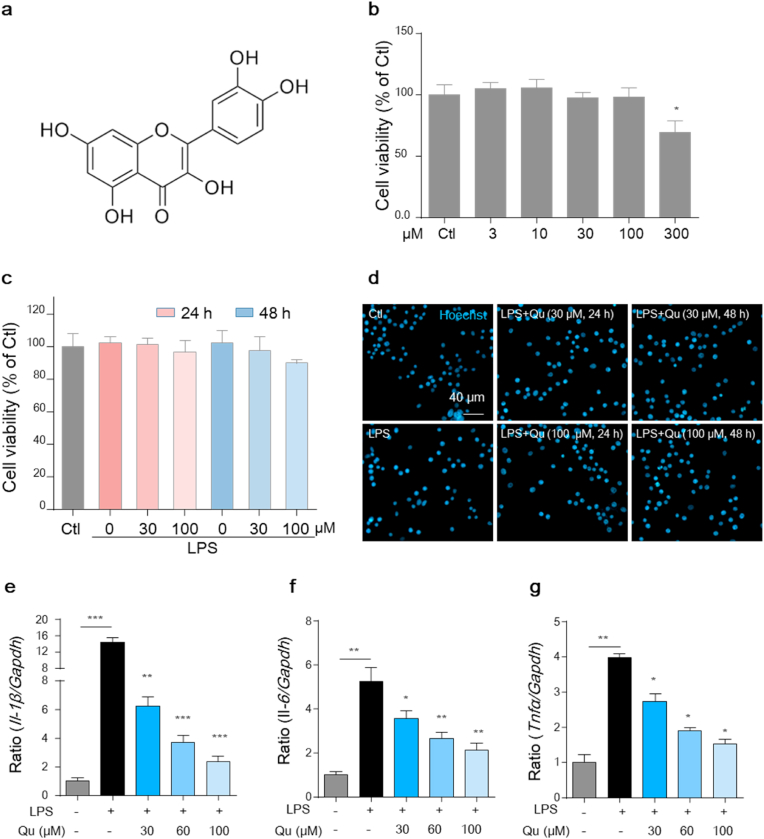
Fig. 1.
Qu suppresses the inflammatory activation in microglial BV2 cells.
(a) The chemical structure of quercetin. (b) BV2 cells were treated with Qu (0–300 μM, 24 h), and then the CCK-8 assay was performed to determine cell viability. (c–d) Cells were treated with Qu (0–100 μM) for 1 h followed by LPS (100 ng/ml) exposure for 24 or 48 h. Cell viability was assessed by the CCK-8 assay (c) and Hoechst staining (d). Scale bar, 40 μm. (e–g) Effects of LPS and Qu on the expression of IL-1β (e), IL-6 (f) and Tnfα (g) in BV2 cells as analyzed by qPCR (normalized to the control group). Data are shown as the e ± SEM and are representative of at least three independent experiments. ns, not significant,*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. Ctl, untreated control; Qu, quercetin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide.