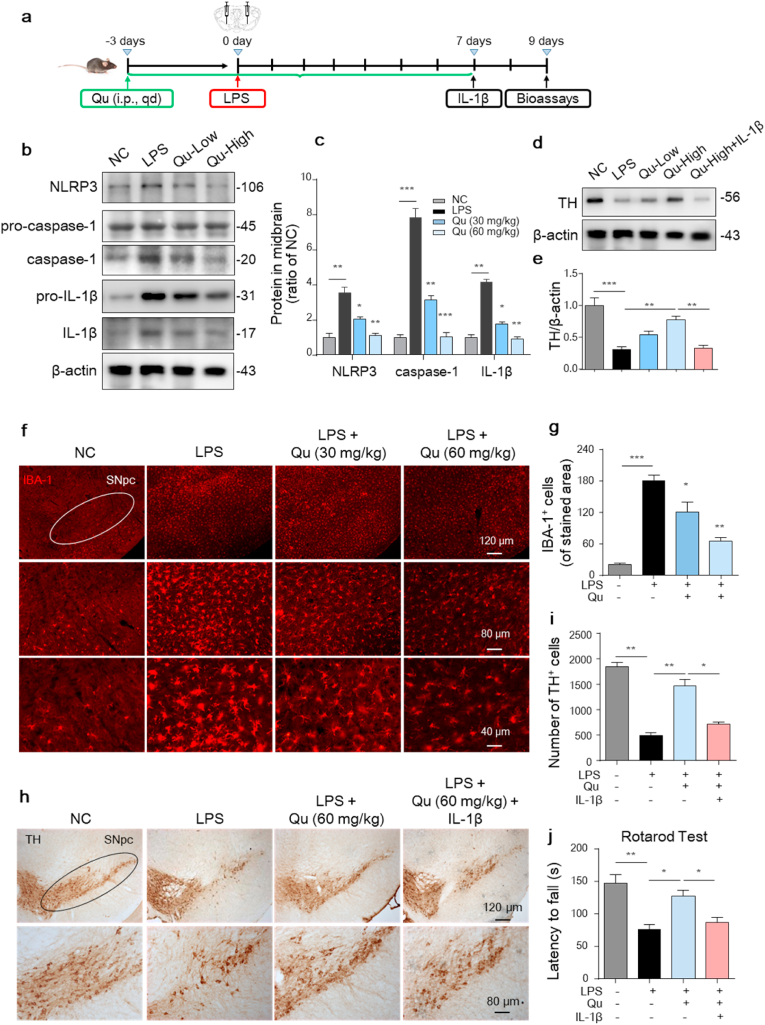
Fig. 9.
Inhibitory effect of Qu on NLRP3 inflammasome activation-related neurotoxicity in LPS-induced PD mice.
(a) Timeline of the experimental procedure in the LPS-induced mouse PD model.
(b–c) Protein levels of NLRP3, caspase-1, pro-IL-1β and IL-1β in mouse mesencephalic homogenates were analyzed by western blot (b) and quantified (c). Low indicated 30 mg/kg b.w., high indicated 60 mg/kg b.w. dose.
(d–e) Expression of TH protein levels in mesencephalon from the indicated mice was analyzed by immunoblotting (d) and quantitative analyzed (e).
(f–g) Immunofluorescent staining of IBA-1-positive microglia in SNpc sections (f) and quantitative analyzed (g). Scale bars as indicated.
(h–i) Immunohistochemical images of TH-positive DA neurons in SNpc sections (h) with quantification (i). Scale bars as indicated.
(j) Rotarod test in different groups at the end of the experiment. (n =
7–
9 mice/group).
Values are shown as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. n = 4–6 mice per group in (b–i). NC, negative control; Qu, quercetin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; SNpc, substantia nigra pars compacta.