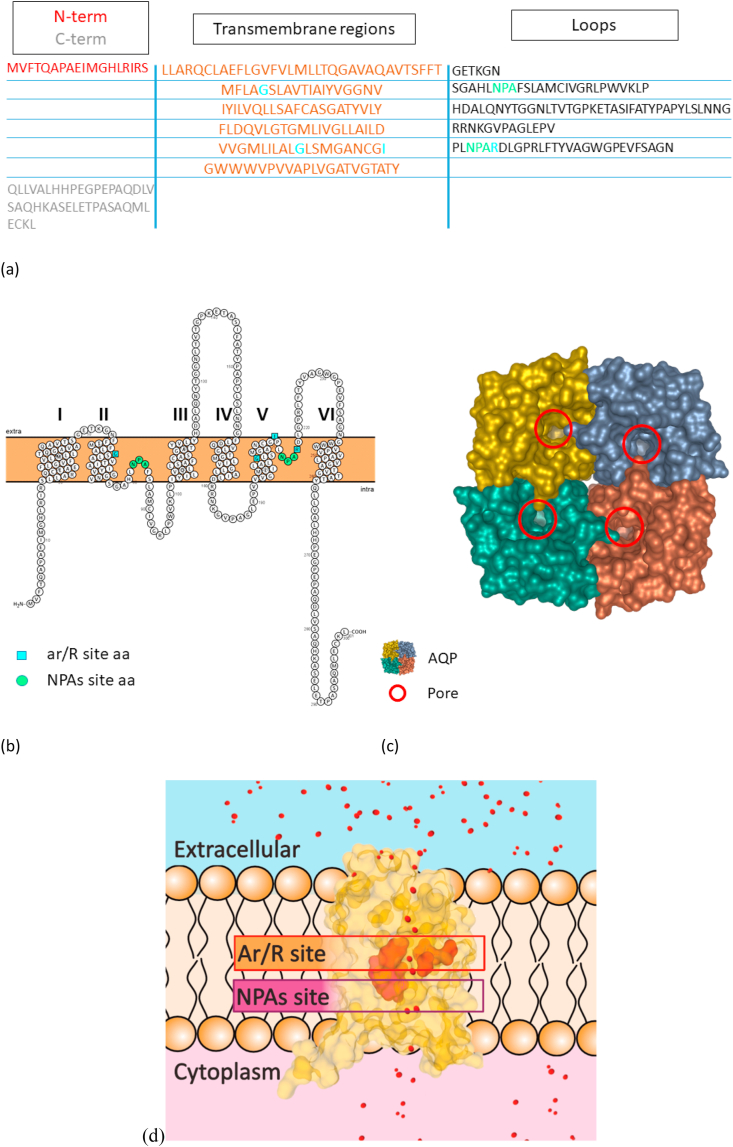
Fig. 1.
General structure of AQPs on the basis of AQP10. Panel (a) shows the sequence of AQP10 monomer, highlighting the 6 transmembrane regions, loop regions and the N- and C- terms. Panel (b) shows a 2D representation of AQP10 monomer sequence performed with Protter [16]. The transmembrane regions are numbered from 1 to 6. The 2 NPAs, despite their position in the loops, are situated in the plasma membrane. NPAs are essential components of the AQPs funnel, together with the ar/R constriction site. N-term and C-term are usually orientated intracellularly, on the same side of the membrane. In panels (a) and (b) NPAs residues are highlighted in green, ar/R residues are highlighted in light blue. The prediction of the transmembrane regions is based on sequence analysis performed with MPEx tool [17]. Panel (c) is a 3D representation of AQP10 tetramer. The red circles highlight the pore entry in each of the monomers. Panel (d) shows the conformation of a AQP10 monomer located in the plasma membrane. The internal part of the funnel is the most important for the determination of AQPs selectivity. The NPA motifs central position in the pore narrow its diameter and it is believed to have role in the prevention of proton free flow through the channel. On the side of the funnel towards the extracellular entrance there is a second conserved region, the aromatic/R site, which is considered the dimensional and selectivity filter. In the superaquaporins the arginine is substituted by a leucine, yielding NPL motif. Panels (c) and (d) are based on the RCSB PDB [18] crystal structure of AQP10 (PDB ID: 6F7H) published by Gotfryd et al. [19]; the images has been prepared with the use of mol* software [20]. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)