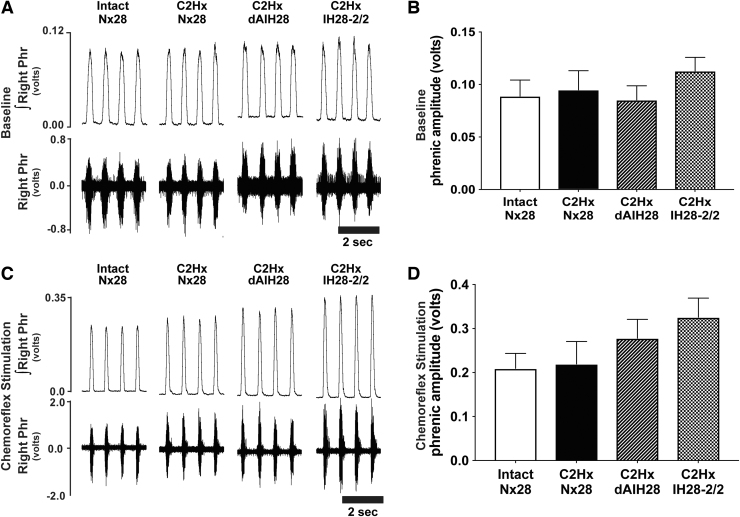
FIG. 3.
Right phrenic nerve activity (contralateral to C2 hemisection) during baseline and chemoreflex stimulated conditions. (A) Representative compressed traces depict raw (bottom) and integrated (top) right phrenic (i.e., contralateral to injury) neurograms under baseline conditions from intact rats, and rats with chronic C2 hemisection (C2Hx) exposed to 28 days of normoxia (Nx28), daily acute intermittent hypoxia (dAIH28), or chronic intermittent hypoxia simulating moderate sleep apnea (IH28-2/2). (B) Under baseline conditions, average contralateral/right integrated phrenic burst amplitude (volts) in C2Hx rats was not different from intact rats exposed to Nx28. No protocol-specific differences were observed across groups. (C) Representative traces depict raw and integrated right phrenic neurograms under hypercapnic chemoreflex stimulated conditions. (D) During chemoreflex stimulation, average contralateral/right integrated phrenic burst amplitude was not different between intact vs. injured rats. No protocol-specific differences were observed across groups.