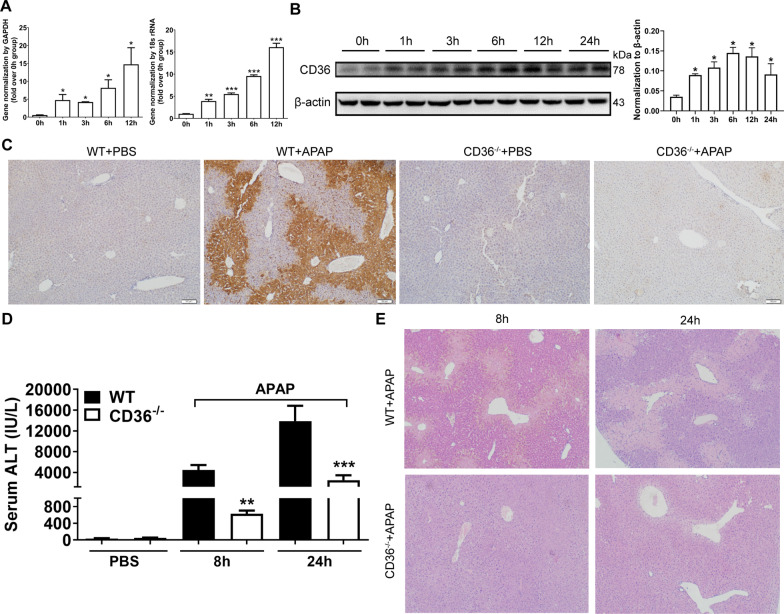
Fig. 1.
CD36 deficiency reduced APAP-induced murine liver injury. WT mice were starved for 16 h and i.p. injected with APAP at 300 mg/kg. The expression of CD36 in the liver at specified time point after APAP treatment was determined by A q-PCR and B Western blotting. *p < 0.05, compared with 0 h; C Immunohistochemical staining of CD36 in the liver sections of mice treated with PBS or APAP for 24 h. D Serum ALT and E liver H&E staining at 8 h and 24 h after APAP injection in mice. N = 6–8 mice per group. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared with WT mice