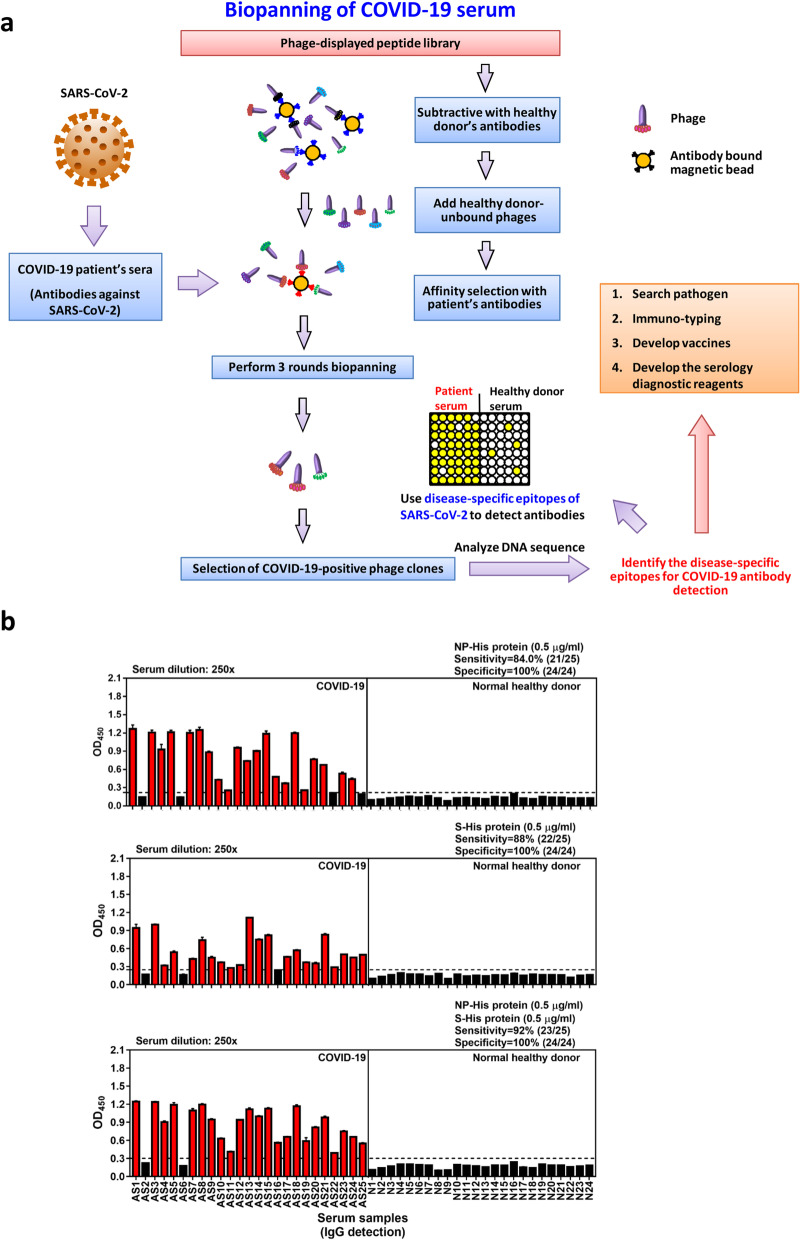
Fig. 1.
Biopanning phage-displayed peptide library with COVID-19 patient serum samples. a Illustration shows the strategy for biopanning disease-specific B-cell epitopes. Serum samples of COVID-19 patients and normal healthy donors were used to prepare IgG-captured magnetic beads. The phage-displayed peptide library was pre-cleaned by normal healthy serum (NHS) IgG-coated magnetic beads, and three rounds of affinity selection of NHS-unbound phages were performed using COVID-19 IgG-magnetic beads. After biopanning, immunopositive phage clones were validated with ELISA and DNA sequenced. The disease-specific epitopes were further identified and characterized by bioinformatic prediction of B-cell epitopes, structural analysis and SARS-CoV-2 protein/peptide synthesis for binding and competitive-inhibition assays. Information about disease-specifc epitopes will be helpful for pathogen research, immune-typing, development of vaccines and serology diagnostic reagents. b Serological detection of COVID-19 convalescent patient antibodies using SARS-CoV-2 NP and extracellular domain of spike recombinant proteins. Horizontal dashed line denotes the cutoff value (calculated as mean OD450 + 4 × SD of normal healthy serum samples) for recombinant SARS-CoV-2 NP or extracellular domain of S protein. Immunopositive cases are colored red