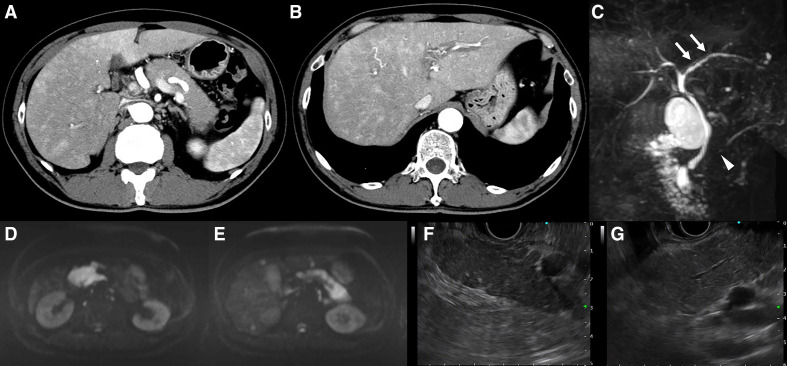
Figure 1.
Findings of radiological imaging: contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT), magnetic resonance cholangial pancreatography (MRCP) and endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS). (A) CECT. Sausage-like swelling of the whole pancreas, characterised by a lack of increase in the surrounding adipose tissue and low absorption in the early phase of contrast. No capsule-like rim was observed. (B) Liver parenchyma showing strong staining around the bile duct in the early phase of contrast, suggesting cholangitis. This observation was more intense in the right liver lobe than in the left. A periportal colour sign was also recognised. (C) MRCP. Appearance of beads in the left intrahepatic bile duct (arrow) and localised narrowing in the head and the body of the main pancreatic duct (arrowhead). (D, E) Examination of the whole pancreas revealing a remarkably high signal in diffusion weighted imaging. (F) EUS. Pancreatic swelling accompanied by lobularity with honeycombing, and hyperechoic foci without shadowing in the pancreatic parenchyma. (G) Hyperechoic main pancreatic duct margin in the main pancreatic duct.