Figure 1. Generation of a zebrafish chd7 mutant using CRISPR/Cas9.
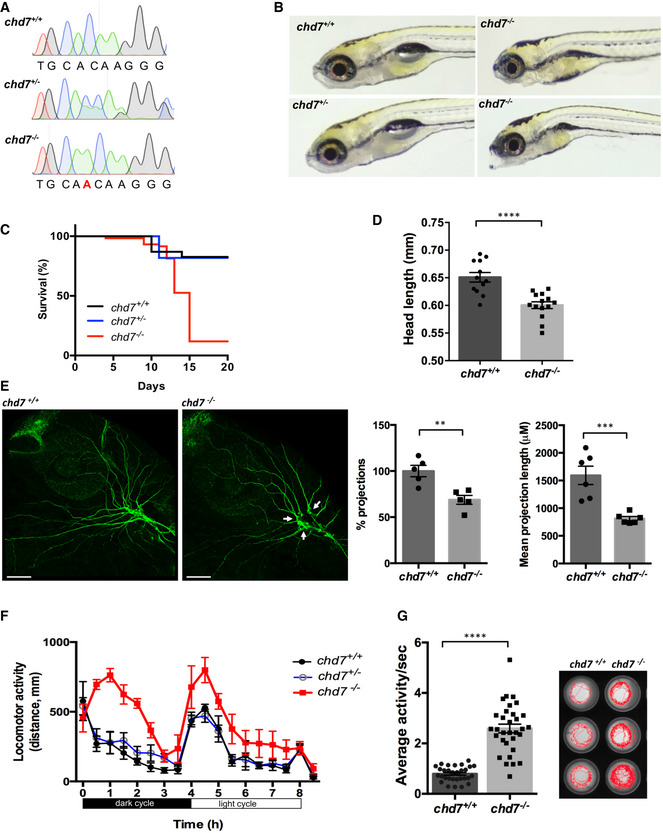
- Chromatograms showing the confirmation a 1‐nucleotide insertion mutation by Sanger sequencing.
- Gross morphological analyses of control (chd7 +/+; top left image), heterozygous (chd7 +/−; bottom left image) and knockout mutants (chd7 −/−; images in right panel).
- Kaplan–Meier survival plot showing low survival of chd7 mutants after 12 dpf (N = 5).
- Measurement of head size of control (n = 12) and mutants (n = 14) showing significantly smaller head size in chd7 −/− fish (****P < 0.0001, Student’s t‐test).
- Acetylated tubulin staining in 28 hpf controls (left) and mutants (right) showing severely affected outbranching of the trigeminal nerve (Vth cranial nerve). Notably, chd7 −/− display reduced branching of the Vth cranial nerve (arrows) and axonal arborization in the tectal area. Graphs showing quantitative analyses of percentage (n = 5) and mean total length of peripheral projections (n = 6) per zebrafish in controls and mutants (***P < 0.001; **P < 0.005, Student’s t‐test).
- Locomotor activity of control (black), heterozygous (blue) and mutants (red) showing significant hyperactivity of mutants in dark and light cycles (N = 3, n = 48).
- Average activity per second during dark cycle (left) is significantly increased in chd7 −/− mutants compared with chd7 +/+ (n = 32; ****P < 0.0001, Student’s t‐test). Representative swimming tracks during dark cycle of control and mutant fish (right). Mutant chd7 −/− larvae displayed hyperactive swimming.
Data information: ****P < 0.0001; ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.005, Student’s t‐test. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Scale bar = 50 μm. n represents number of fish. N represents number of experimental repeats.
