Figure 4.
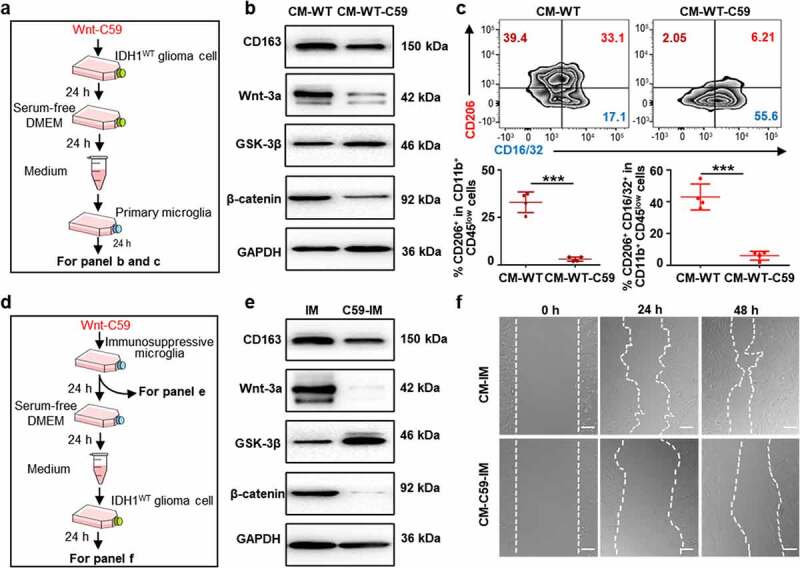
Wnt/β-catenin signaling blockade inhibits IDH1WT GBM migration and proliferation by abolishing immunosuppressive microglia. (a) Schematic illustration showing the treatment of primary microglia with conditioned medium from IDH1WT GL261 cells (CM-WT) or medium from IDH1WT GL261 cells pretreated with Wnt-C59 (CM-WT-C59) for 24 h. Immunoblots of primary microglia after the corresponding treatments are shown in panel (b). (c) Flow cytometric analysis of CD11b+CD45low cells after the corresponding treatments (n = 4). Mean±SD are shown. (d) Schematic illustration of the treatment of IDH1WT GL261 cells with conditioned medium from immunosuppressive microglia (CM-IM) or Wnt-C59-pretreated immunosuppressive microglia (CM-C59-IM). (e) Immunoblots of Wnt-C59- or F12/DMEM-treated immunosuppressive microglia. (f) Wound healing assay showing IDH1WT GL261 cell monolayers at 24 h after treatment with CM-IM or CM-C59-IM. Scale bar, 100 μm. All values are shown as Mean±SD. Student’s t-test. ***p < .001. CM-WT: conditioned medium from IDH1WT GL261 cells; CM-WT-C59: conditioned medium from Wnt-59-treated IDH1WT GL261 cells; IM: immunosuppressive microglia; C59-IM: Wnt-59-treated immunosuppressive microglia; CM-IM: conditioned medium isolated from immunosuppressive microglia; CM-C59-IM: conditioned medium from Wnt-59-treated immunosuppressive microglia
