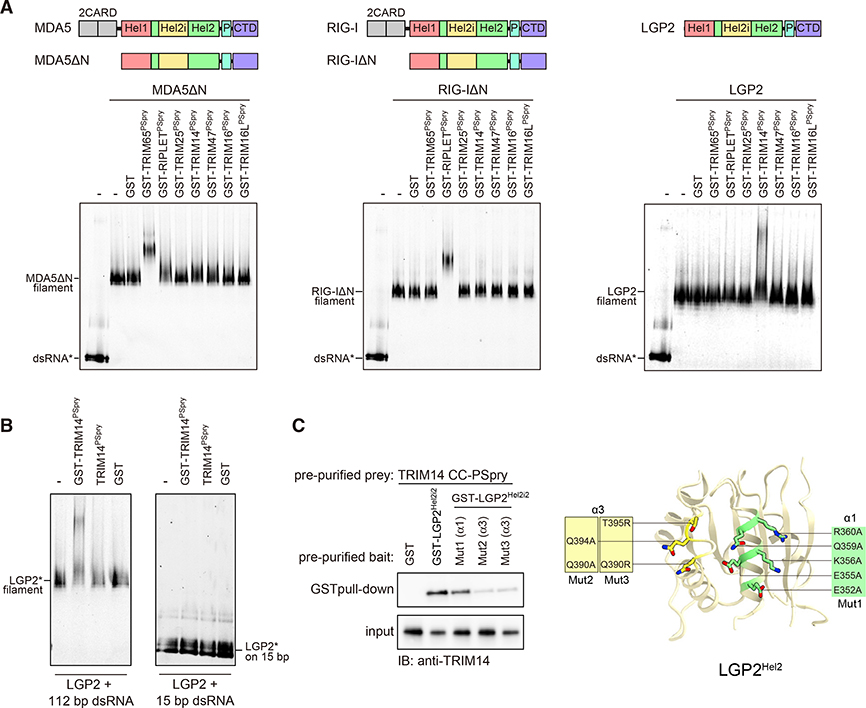
Figure 5. LGP2 is recognized by TRIM14 via PSpry bivalency and Hel2 epitope.
(A) Native gel mobility shift assay to test interactions between RLR filaments and a panel of TRIMPSpry closely related to those of RIPLET and TRIM65 (Figure S6). RLR filaments were formed by mixing MDA5ΔN, RIG-IΔN, and LGP2 (250 nM) with Cy5-labeled (*) 112-bp dsRNA (1 ng/μL) and incubated with TRIMPSpry fused with GST (300 nM for RIG-I/MDA5 and 1.2 μM for LGP2). Cy5 fluorescence was used for gel imaging.
(B) Mobility shift assay of LGP2 (0.6 μM) bound to 112-bp or 15-bp dsRNA (2.4 ng/μL) in the presence of GST-TRIM14PSpry, TRIM14Pspry, or GST alone (2.4 μM).
(C) GST pull-down assay to examine the interaction between GST-LGP2Hel2i2 and TRIM14CC-PSpry. GST-LGP2Hel2i2 and TRIM14CC-PSpry were recombinantly expressed in E. coli and purified prior to GST pull-down. The variants (Mut1–Mut3) of LGP2Hel2i2 with mutations in the α1 and α3 helices are defined on the right. Mutated residues are mapped onto the modeled human LGP2 Hel2, which was built using the Phyre2 server (http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk) with the crystal structure of chicken LGP2 (PDB: 5JB2) as a template.