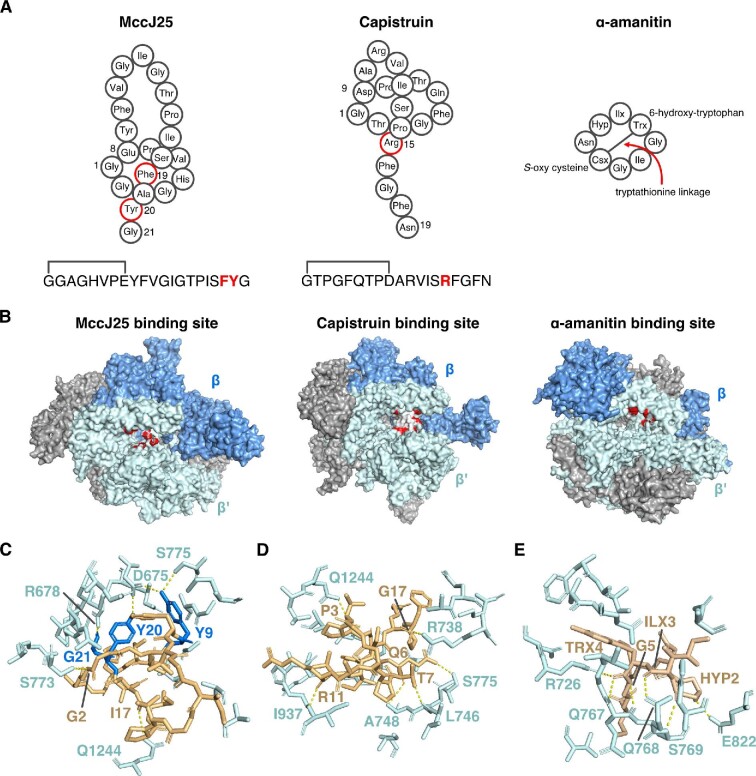
Fig. 9.
RiPP inhibitors of RNA polymerase (RNAP). (A) Schematics of microcin J25 (MccJ25), capistruin, and α-amanitin. ILX: 4,5-dihydroxyisoleucine, TRX: 6-hydroxytryptophan, CSX: S-oxy cysteine, HYP: HYP: 4-hydroxyproline. Note the tryptathionine linkage between 6-hydroxytryptophan and S-oxy cysteine. (B) From left to right, crystal structures of E. coli RNAP showing the binding site of MccJ25, E. coli RNAP showing the binding site of capistruin, and yeast RNA polymerase II (Pol II) showing the binding site for α-amanitin. Residues in RNAP or Pol II that directly contact these RiPPs are colored red. (C) Zoomed-in view of MccJ25 (gold/blue) bound to RNAP (cyan). Key amino acids for this interaction are labeled. Dashed lines are H-bonds (yellow). (D) As in part C, but for the RNAP–capistruin interaction. (E) Zoomed-in view of the α-amanitin-Pol II binding site with key interacting residues highlighted. HYP: hydroxyproline, ILX: dihydroxyisoleucine, TRX: hydroxytryptophan. Drawn from PDB files 6N60 (MccJ25), 6N61 (capistruin), and 3CQZ (α-amanitin).