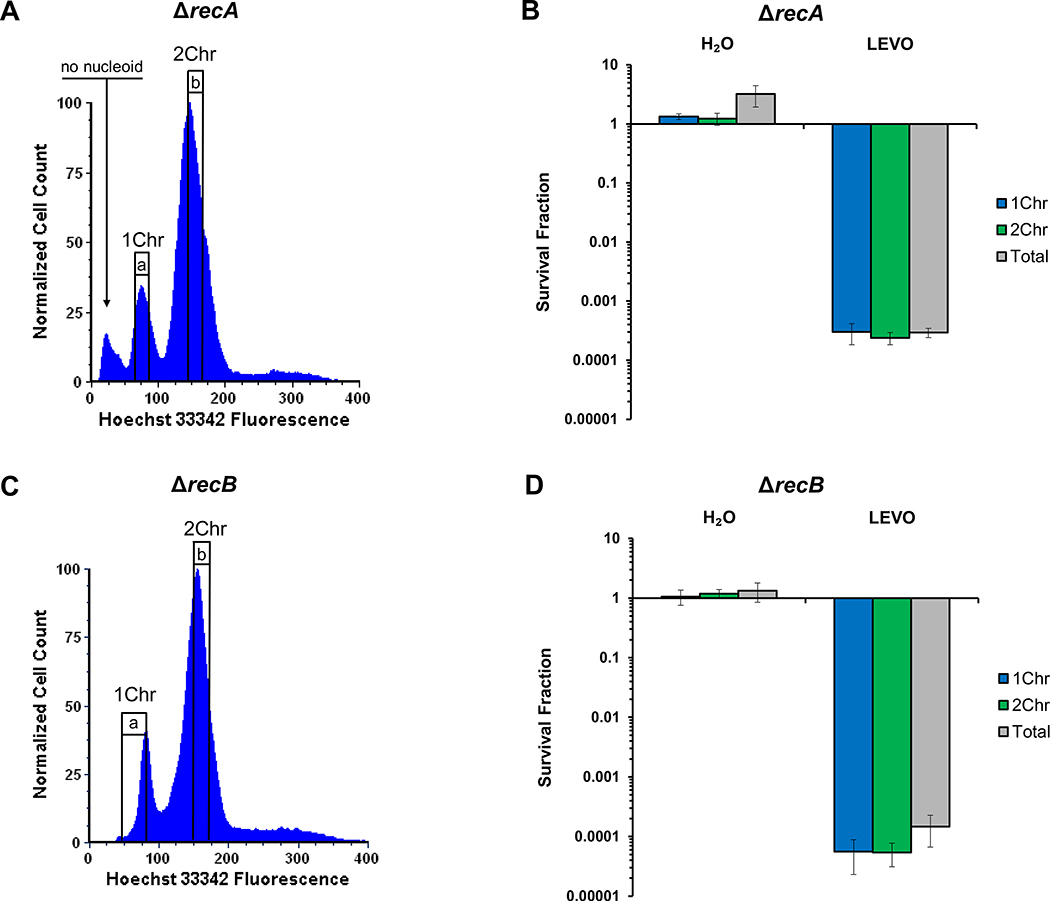
Figure 4. Chromosomal association with FQ persistence eliminated in HR mutants.
(A) Representative DNA histogram of a stationary-phase population of MG1655 ΔrecA stained with 5 μg/mL Hoechst 33342. The small peak (arrow) that is less fluorescent than the 1Chr peak was not culturable after sorting and has been previously described as cells without nucleoids35. (B) When sorted and treated with 5 μg/mL LEVO, the association between chromosomal content and persistence was eliminated in a MG1655 ΔrecA mutant (n = 3). (C) Representative DNA histogram of a stationary-phase population of MG1655 ΔrecB stained with 5 μg/mL Hoechst 33342. (D) No association between chromosomal content and persistence was observed in a MG1655 ΔrecB mutant treated with 5 μg/mL LEVO (n = 3). Raw CFU/mL values and additional controls can be found in Figure S4. 1Chr and 2Chr indicate chromosome number as determined by experiments presented in Figure 2. Representative gating strategies are indicated by a and b. Error bars portray ± SEM. All replicates were independent biological replicates. No statistical significance was achieved as determined using a one-way ANOVA (ΔrecA: F(2,6) = 0.15, p = 0.86; ΔrecB: F(2,6) = 0.38, p = 0.70).