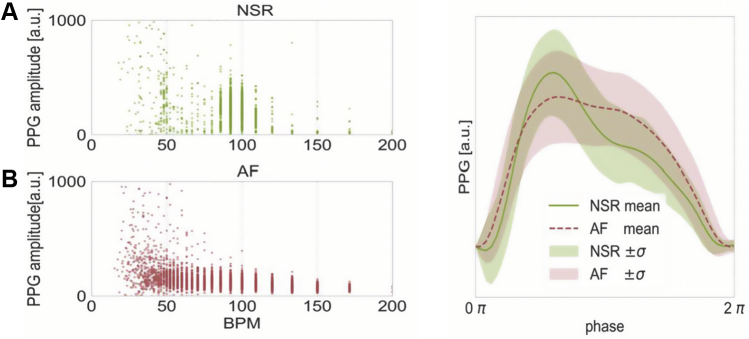
Figure 4.
Waveform morphology of a single patient in atrial fibrillation (AF) and normal sinus rhythm (NSR). Morphologic differences are shown. Left: Variability in heart rate and photoplethysmography (PPG) amplitude for a randomly selected patient who was successfully cardioverted, during AF (A) and NSR (B). AF (red in B) is characterized by greater heart rate variability and lower amplitude. The x-axis represents beats per minute (BPM), which is calculated as the inverse of the time between consecutive minima. The y-axis is the PPG amplitude in arbitrary units (a.u.). Right: Morphologic characteristics of the patient’s mean heart rate cycle, using resampling to equate the time domain. It is visually evident that the morphology differed during AF and NSR for this representative patient.