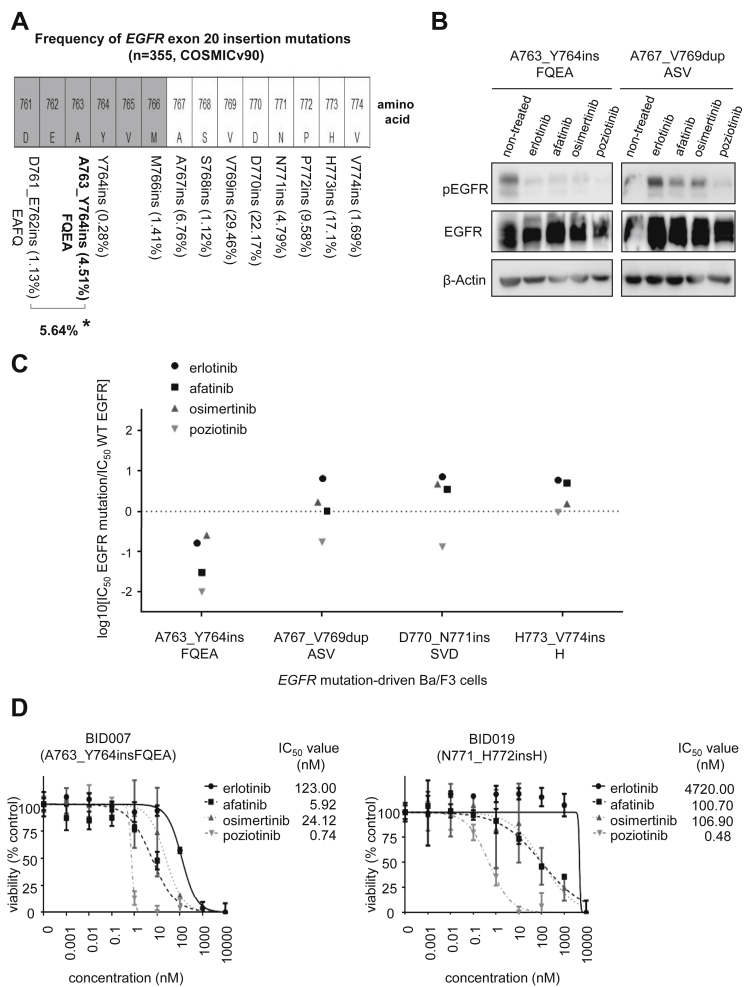
Figure 1.
Preclinical models of EGFR exon 20 insertions mutations. (A) Schematic representation of the amino acids that span the kinase domain of EGFR within the site of EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. The gray-shaded amino acids are part of the C-helix of EGFR whereas the white bars indicate amino acids in the loop following the C-helix (where most EGFR exon 20 insertions are located). The mutation frequency distribution was calculated using COSMIC v90 (http://cancer.sanger.ac.uk) using the following filters: NSCLC, adenocarcinoma, exon 20 insertions (n = 355). Asterisk (∗) indicates combined frequency of EGFR-A763_Y764insFQEA mutation and the identical amino acid sequence of EGFR-D761_E762insEAFQ. (B) Western blotting of Ba/F3 cells driven by EGFR-A763_Y764insFQEA and EGFR-A767_V769dupASV. Cells were treated with EGFR TKIs for 8 hours at the following concentrations: 1000 nM of erlotinib, 40 nM of afatinib, 3 nM of osimertinib, and 5nM of poziotinib. pEGFR at position 1068, total EGFR and β-Actin as a loading control are exhibited. (C) Therapeutic window of different EGFR TKIs to EGFR exon 20 mutations. Cells were plated at a density of 5000 cells per well (96-well plates) and grown over 72 hours after treatment. Logarithm of the 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of EGFR exon 20 mutants compared with wild-type EGFR is plotted (three separate experiments were used to generate IC50). Values below 0 indicate sensitivity whereas values above 0 indicate resistance to EGFR TKIs. The relative sensitivity of EGFR-A763_Y764insFQEA to EGFR TKIs when compared with more frequent TKI-sensitizing mutations (such as EGFR exon 19 deletions, L858R, G719A, L861Q, and S768I) can be found in reference Udagawa et al.6(D) Dose-response proliferation assays (percent viability) for patient-derived lung cancer cell lines harboring EGFR-A763_Y764insFQEA (BID007) and EGFR-N771_H772insH (BID019) after exposure to increasing concentrations of EGFR TKIs. Cells were plated at a density of 7500 cells per well (96-well plates) and grown over 72 hours after treatment. Median IC50 and SD (error bars) of three separate experiments are exhibited. Results from B, C, and D confirm that EGFR-A763_Y764insFQEA—unique among other EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations—is a sensitizing mutation to approved and in-development EGFR TKIs. COSMIC, Catalog of Somatic Mutations in Cancer; IC50, concentration that inhibits 50%; pEGFR, phosphorylated EGFR; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; WT, wild-type.