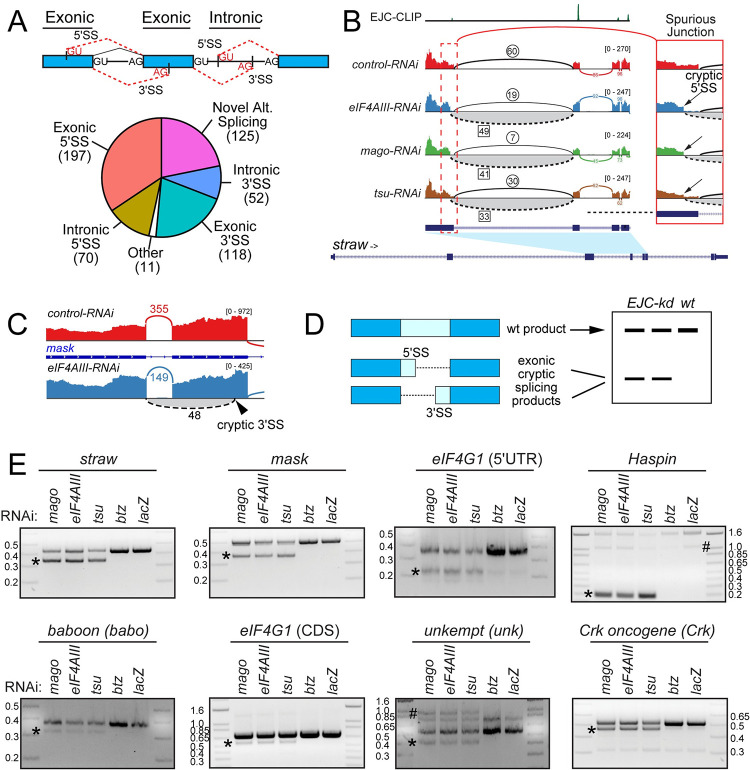
Fig 1. Transcriptome-wide de novo alternative splicing upon depletion of functional Exon Junction Complex.
(A) Overview of upregulated de novo splice junctions in EJC-depleted cells. Top: schematic of cryptic 5’ and 3’ SS. In this toy gene model, canonical pre-mRNA exons and introns are depicted as blue boxes and black lines. The ends of these introns are marked by splice signatures (GU: donor and AG: acceptor, shown in black). Cryptic splice sites identified in the EJC LOF datasets can be found within sequences that are normally exonic or intronic. These sites and the putative de novo intron are shown as red text and dashed lines. Bottom: Pie chart indicating the distribution of different splice junction classes. (B) Sashimi plot depicting HISAT2-mapped sequencing coverage along a portion of straw, which has defective splicing under core-EJC LOF. The gene model depicts the location of the cryptic 5’ SS relative to the annotated 5’ SS. Junction spanning read counts mapping to the canonical junction are circled, whereas cryptic junction read counts are squared. Note that spliced reads mapping to the cryptic junction are found in eIF4AIII-, mago- and tsu-KD but not the control comparison. EJC-CLIP [29] shows recruitment of EJC to exon-exon junctions. Region containing the cryptic 5’ SS has been zoomed on the right. (C) Sashimi plot depicting RNA-seq coverage at the mask gene, where depletion of the EJC (shown here, eIF4AIII-RNAi) results in utilization of a cryptic exonic 3’ SS. (D) Schematic for rt-PCR validation of exonic cryptic splicing, which yields shorter, internally deleted products. (E) Validation of de novo splicing events in core-EJC depleted cells. EJC core components (eIF4AIII, mago, tsu and btz) were depleted from Drosophila S2 cells using dsRNA. After knockdown, eight targets identified in (A) were evaluated using rt-PCR and demonstrated splicing defects (asterisk). Importantly, only knockdown of core-EJC factors yielded cryptic bands, but not btz or control conditions. unkempt (unk) generates several products due to multiple alternative exons included within its rt-PCR amplicon (S1D Fig). # indicates products of unknown identity.