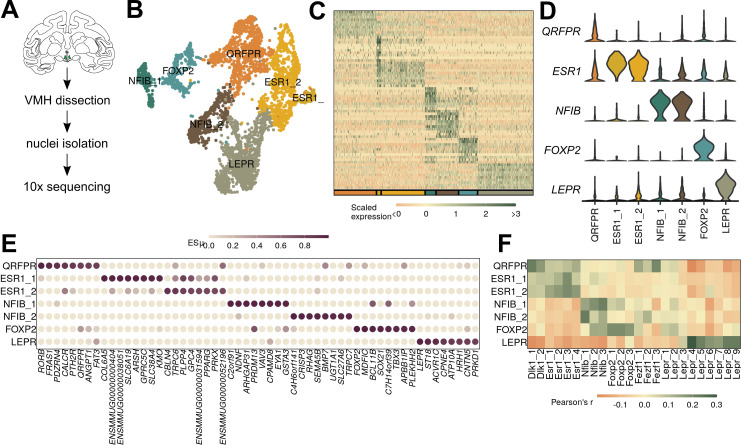
Figure 4. Macaque ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus (VMH) populations revealed by single-nucleus RNA-sequencing (snRNA-seq).
(A) Schematic of experimental process for macaque snRNA-seq. (B) UMAP of 3752 VMH neuronal nuclei colored and labeled by cluster designation. (C) Expression profile of the top enriched genes for each cluster. (D) Violin plot of normalized expression for marker genes for each VMH neuronal population. (E) ESµ for the top five marker genes for each cluster determined by CELLEX. (F) Pairwise scaled expression correlation (Pearson’s r) for each macaque and mouse VMH neuronal cluster.